What is volumetric flow meter
A volumetric flow meter is an instrument that can measure the volume of fluid passing through the measurement location within a set period of time. A positive displacement flowmeter as a mechanical flow meter is a common type of Volumetric Flow Meter. It can measure the volume flow of high viscosity and corrosive fluids.

How does a volumetric flow meter work ?
The positive displacement flow meter is a flow meter that uses mechanical measuring elements to continuously divide the fluid into a single known volume, and repeatedly fill and discharge the volume of fluid to accumulate the total amount of fluid.
Under the conditions of a given flow meter, the volume of the metering space is determined. As long as the number of rotations of the rotor is measured, the cumulative value of the volume of fluid passing through the flow meter can be obtained.
types of positive displacement flowmeter
In order to meet the requirements of various media and different working conditions for flow measurement in production, various types of positive displacement flowmeters have been produced. Among them, there are three types of gear flowmeters, dual rotor flowmeters and waist wheel flowmeters.
1. Gear Type Positive Displacement Flowmeter
Oval gear flowmeter is also called fixed displacement flowmeter, referred to as PD flowmeter. The casing of this flowmeter is equipped with two rotors, which are directly or indirectly meshed with each other, and rotate under the action of the pressure difference between the inlet and the outlet of the flowmeter. Through the rotation of the gear, the fluid filled in the “metering space” between the gear and the housing is continuously discharged. By measuring the number of rotations of the gear, the amount of fluid passing through the flowmeter can be obtained. The oval gear flowmeter has high measurement accuracy and is suitable for measuring the flow of high-viscosity media, but it is not suitable for fluids containing solid particles (solid particles will jam the gear, making it impossible to measure the flow). If the measured liquid medium contains gas, it will also cause measurement errors.
2. Double rotor (screw) flowmeter
Dual-rotameter flowmeters are the latest generation of positive displacement flowmeters, also known as UF —” flowmeters or screw flowmeters. It is especially suitable for thin oil, light oil, heavy oil, crude oil with large sand content and large water content. The viscosity range of the liquid to be measured is large. The metering flowmeter of industrial liquids can be indicated on site, and the code can be read directly and can be distributed. It can output electric pulse signal, which is transmitted to secondary instrument or computer to form automatic control, automatic detection and data processing system.
3. Waistwheel flowmeter
The waist wheel flowmeter is also called the Roots flowmeter. The waist wheel flowmeter is mainly used for the flow measurement of large-diameter gas, liquid, and steam medium fluids in industrial pipelines in various industries. The waist wheel flowmeter can be used for flow measurement of various clean liquids, especially for oil measurement, and can also be made into a flowmeter for measuring gas. Its meter has the highest accuracy, up to 0.1-0.5 level. Its main disadvantages are: large volume, heavy weight, large pressure loss, large vibration during operation, etc.
VOLUMETRIC FLOW METER WORKING PRINCIPLE
The working principle of the positive displacement flowmeter:
when the fluid passes through the flowmeter, a certain pressure difference will be generated between the inlet and outlet of the flowmeter. The rotating part of the flowmeter (referred to as the rotor) rotates under the action of this pressure difference and discharges the fluid from the inlet to the outlet. During this process, the fluid fills the “metering space” of the flowmeter again and again, and is then continuously sent to the outlet. Under the conditions of a given flow meter, the volume of the metering space is determined as long as the number of rotations of the rotor is measured. The cumulative value of the volume of fluid passing through the flowmeter can then be obtained.
The working principle of oval gear flow meter:
The two oval gears have a special shape that rolls against each other for contact rotation. P1 and p2 represent the inlet pressure and the outlet pressure, respectively. Obviously, p1>p2. The lower gear in Figure 1(a) rotates counterclockwise under the action of the pressure difference on both sides, which is the driving gear; the upper gear is equal to the pressure on both sides. No rotational torque is generated, it is a driven wheel, which is driven by the lower gear and rotates clockwise. At the position shown in Figure 1(b), both gears generate rotational torque under the action of differential pressure and continue to rotate. When it is installed in the position shown in Figure 1(c), the upper gear becomes the driving wheel, and the lower gear becomes the driven wheel, which continues to rotate to the same position as shown in Figure 1(a) to complete a cycle. One cycle action expels the fluid volume of the four crescent-shaped cavities enclosed between the gear and the housing wall, which is called the “cycle volume” of the flowmeter.
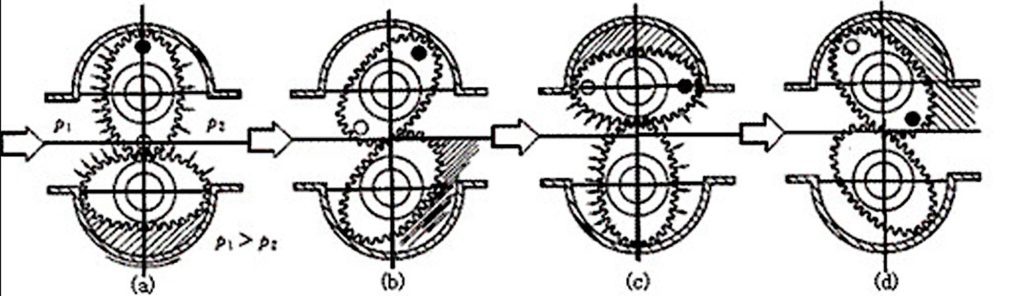
How Oval Gear Flow Meters Work ?
Let the “circulation volume” of the flowmeter be υ, and the number of gear rotations in a certain period of time is N, then the volume of fluid flowing through the flowmeter during this time is V,
Then V=Nυ (1)
The rotation of the oval gear is transmitted to the counter through the magnetic seal coupling and the transmission reduction mechanism to directly indicate the total amount flowing through the flowmeter. If the sending device is attached, and the electric display instrument is added, the remote transmission is only instantaneous flow or cumulative flow.
The working principle of the Roots flowmeter of the waist wheel flowmeter:
The waist wheel flowmeter is also called the Roots flowmeter. Its structural characteristics are: there is a measuring chamber in the shell of the flowmeter, and there are one or two pairs of waist wheels that can rotate tangentially in the measuring chamber. A pair of transmission gears are installed coaxially with the two search wheels outside the casing of the flowmeter, and they mesh with each other so that the two waist wheels can be linked with each other. There is a constant flow of fluid separated by the side and elements and sent from the inlet to the outlet. Just know the volume of the metering chamber space. And record the number of rotations of the waist wheel N. The fluid volume V through the flow basin meter can be obtained. Obviously, for the flow rate of the waist wheel flowmeter: V=4Nv (2-2)
Working principle of double rotor (screw) flowmeter:
A pair of special-toothed helical rotors of the dual-rotor (screw) flowmeter are directly meshed, without relative sliding, and without synchronizing gears. The rotor is driven to rotate by a small pressure difference at the inlet and outlet. Therefore, the number of revolutions of the rotor is proportional to the cumulative flow of the fluid, and the rotational speed of the rotor is proportional to the instantaneous flow of the fluid. The number of revolutions of the rotor is transmitted to the meter counter through the magnetic coupling, which shows the flow through the flow meter (through the pipeline).
The dual rotor (screw) flowmeter is a uniquely designed positive displacement flowmeter mainly used for liquid flow measurement.
Where are the positive displacement used for?
Positive displacement flow meters are particularly suitable for the flow of viscous fluids such as oil, condensate, resins and liquid foods. For the flow of high viscosity medium, other flowmeters are difficult to measure, but positive displacement flowmeters can accurately measure the accuracy of ±0.2%. Therefore, positive displacement flowmeters are often used in the total measurement of expensive media (oil, natural gas, etc.).
POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT VOLUMETRICFLOW METER APPLICATION
Application of positive displacement flowmeter:
Positive displacement flowmeter, differential pressure flowmeter and float flowmeter are listed as the three most widely used flowmeters, and are often used in the total measurement of expensive media (oil, natural gas, etc.).
Commonly used volumetric flowmeters include oval gear flowmeters, dual rotor flowmeters, and waist wheel flowmeters.
Applications of oval gear flowmeters:
Oval gear flowmeter (also known as displacement flowmeter, gear flowmeter) is a kind of positive displacement flowmeter, and it is a kind of high precision flowmeter. The oval gear flowmeter can be made of different materials (cast iron, cast steel, 304 stainless steel, 316 stainless steel) for precise continuous or intermittent measurement of liquid flow or instantaneous flow in pipelines. The oval gear flowmeter is especially suitable for flow measurement of heavy oil, polyvinyl alcohol, resin and other media with higher viscosity, such as flow measurement in chemical, petroleum, pharmaceutical, electric power, metallurgy and food industries.
Application of dual rotor flowmeter:
The dual-rotor flowmeter belongs to the latest generation of positive displacement flowmeters in the world, also known as UF-‖ flowmeters or screw flowmeters. Double rotameter is a precision instrument for the measurement and control of liquid flow in pipelines. Widely used in petroleum, chemical, metallurgy, electric power, transportation, ships, oil depots, terminals, tank trucks and other departments, especially for crude oil, refined oil, light hydrocarbons and other industrial liquids. The metering flowmeter can indicate on-site, and the word code can be read directly and It can be equipped with a transmitter to output electrical pulse signals, which can be transmitted to secondary instruments or computers to form automatic control, automatic detection and data processing systems.
Application of waist wheel flowmeter:
The waist wheel flowmeter is also called the Roots flowmeter. The waist wheel flowmeter is mainly used for the flow measurement of large-diameter gas, liquid, and steam medium fluids in industrial pipelines in various industries. The waist wheel flowmeter can be used for flow measurement of various clean liquids, especially for oil measurement, and can also be made into a flowmeter for measuring gas. Its meter has the highest accuracy, up to 0.1-0.5 level. The waist wheel flowmeter is mainly used in the petroleum and petrochemical industry, oil depot oil platform, wharf, water gas station for loading, shipping, oil sales measurement, quantitative delivery, raw material in and out measurement, fuel consumption, etc.
How to choose the right positive displacement flowmeter?
Choice of Positive Displacement Flowmeter Performance
The following five elements should be considered in the performance selection of positive displacement flowmeter: (1) flow range; (2) physical properties of the measured medium; (3) measurement accuracy; (4) pressure resistance (working pressure) and pressure loss; (5) purpose of use.
⑴ flow range
The flow range of the positive displacement flowmeter is related to the type of the measured medium (mainly determined by the viscosity of the fluid), the characteristics of use (continuous work or intermittent work), measurement accuracy and other factors.
(2) Physical properties of the measured medium
The physical properties of the measured medium mainly consider the viscosity and corrosiveness of the fluid.
⑶ measurement accuracy
Positive displacement flowmeter is one of the flowmeters with the highest measurement accuracy at present.
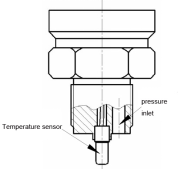
The major influences of site conditions on the measurement accuracy are the influence of the viscosity of the measured medium and the influence of temperature.
⑷ Pressure resistance (working pressure) and pressure loss
The working pressure of the flowmeter should be endured by the flowmeter shell. Different requirements for the working pressure should be used for pressure components of different materials to avoid unsafe use.
⑸ Purpose of use
The flowmeter used for measurement and accounting mainly considers its measurement accuracy, which can be an on-site indicating instrument; the flowmeter used for process control mainly considers its reliability, and should have various supporting equipment such as transmitters, counters, adjustment and display instruments, etc. .
※Note: As one of the earliest flow meter manufacturer, SenTec provide a wide variety flow measurement solutions, such as differential pressure flow meters, Calorimetric Flowmeter, liquid flow sensor, Ultrasonic Level Transmitter, mass flow meter, Variable Area Flowmeter or Rotameter, Electromagnetic Flowmeter, Turbine Flowmeter, Vortex Flow Meter, Thermal Flowmeter, Coriolis Flowmeter, Mass Flowmeters, Open Channel Flowmeters etc.
For specific positive displacement flowmeter price, please contact our sales engineer.