Temperature measurement is a critical aspect of various industrial processes, and RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector) sensors play a pivotal role in ensuring accurate and reliable temperature monitoring. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed understanding of RTD temperature sensor, their functionality, types, testing methods, calibration procedures, wiring and installation techniques, working principles, advantages, and applications.
Understanding RTD Temperature Sensor
RTD temperature sensor is widely used in industrial and scientific applications for precise and stable temperature measurements. Understanding the fundamental principles of RTD sensors is crucial for grasping their significance in temperature monitoring systems. RTD sensors operate on the principle of electrical resistance variation with temperature changes. The most common RTD sensor material is platinum due to its linear resistance-temperature characteristics and stability over a wide temperature range. This section will delve into the basic construction and operating principles of RTD sensors, providing a solid foundation for the subsequent discussions.
The Functionality of RTD Temperature Sensor
The functionality of RTD temperature sensors revolves around their ability to convert temperature variations into measurable electrical signals. This section will elucidate the intricate process by which RTD sensors exhibit changes in electrical resistance in response to temperature fluctuations. The relationship between temperature and resistance, known as the temperature-resistance characteristic curve, defines the core functionality of RTD sensors. By comprehending this relationship, engineers and technicians can harness the full potential of RTD sensors for precise temperature measurements in diverse industrial settings.
Types of RTD Temperature Sensors
RTD temperature sensors are available in various configurations and designs to cater to specific application requirements. This section will explore the different types of RTD sensors, including wire-wound, thin-film, and coiled RTDs, highlighting their unique features and suitability for distinct environments. Understanding the characteristics and limitations of each RTD type is essential for selecting the most appropriate sensor for a particular application, ensuring optimal performance and accuracy.
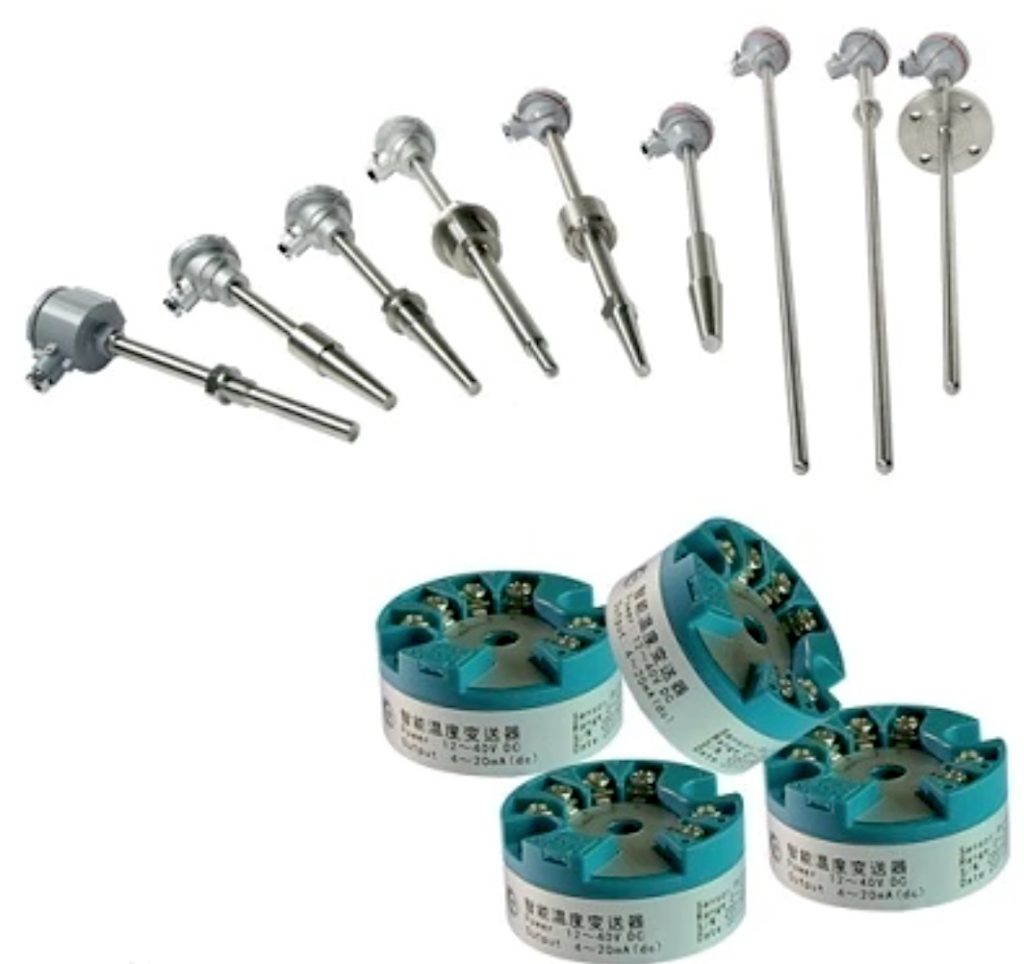

1. Proficient thermal resistance RTD temperature sensor
The structure and characteristics of thermal resistance temperature sensing element (resistor body) commonly used in industry. From the temperature measurement principle of the thermal resistance, it can be known that the change of the measured temperature is directly measured by the change of the resistance value of the thermal resistance. Therefore, the change of the resistance of various wires such as the lead wire of the thermal resistance body will affect the temperature measurement. In order to eliminate the influence of lead resistance, a three-wire or four-wire system is generally used.
2. Armored thermal resistance RTD temperature sensor
The outer diameter of the armored thermal resistance is generally φ2~φ8mm, and the minimum can reach φmm. Compared with ordinary thermal resistance, it has the following advantages:
①Small volume, no air gap inside, and small measurement lag in thermal inertia;
②Good mechanical properties, vibration resistance, impact resistance;
③Can be bent, easy to install
④Long service life.
3. End face thermal resistance RTD temperature sensor
The end-face thermal resistance temperature sensing element is made of specially treated resistance wire, which is closely attached to the end face of the thermometer. Compared with the general axial thermal resistance, it can reflect the actual temperature of the measured end face more accurately and quickly, and is suitable for measuring the end face temperature of bearing bushes and other parts.
4. Flameproof thermal resistance RTD temperature sensor
The explosion-proof thermal resistance uses the special structure of the junction box to confine the explosion of the explosive mixed gas inside the shell due to the influence of sparks or arcs in the junction box, and the production site will not cause an explosion. Explosion-proof thermal resistance can be used for temperature measurement in places with explosion hazards in the Bla~B3c level area.
Testing RTD Temperature Sensors
Before deploying RTD temperature sensors in operational systems, thorough testing is imperative to verify their functionality and accuracy. This section will outline comprehensive testing methodologies for RTD sensors, including resistance measurements, insulation checks, and response time assessments. By following systematic testing procedures, engineers can identify and rectify any potential issues with RTD sensors, ensuring reliable and consistent temperature measurements in industrial processes.
How to Test RTD Temperature Sensors
Testing RTD temperature sensors involves conducting precise measurements to validate their performance characteristics. This section will provide detailed guidelines on how to test RTD sensors using specialized equipment and techniques. From resistance measurements to sensor response evaluations, each testing aspect will be thoroughly elucidated, empowering professionals to conduct rigorous assessments of RTD sensors with confidence and precision.
Calibrating RTD Temperature Sensors
Calibration is a critical process that ensures the accuracy and reliability of RTD temperature sensors throughout their operational lifespan. This section will delve into the intricacies of RTD sensor calibration, covering the calibration standards, procedures, and equipment required for precise temperature measurement. By following best practices in RTD sensor calibration, industries can maintain consistently high levels of measurement accuracy, compliance with standards, and operational efficiency.
Wiring and Installation of RTD Temperature Sensors
Proper wiring and installation are essential for optimizing the performance and longevity of RTD temperature sensors. This section will provide comprehensive guidance on the correct wiring techniques, insulation considerations, and installation practices for RTD sensors in different industrial environments. By adhering to recommended wiring and installation procedures, professionals can mitigate potential measurement errors and ensure the seamless integration of RTD sensors into temperature monitoring systems.
How RTD Temperature Sensors Work
Understanding the working principles of RTD temperature sensors is paramount for harnessing their full potential in temperature monitoring applications. This section will elucidate the intricate mechanisms through which RTD sensors convert temperature variations into electrical signals, covering the role of temperature coefficients, resistance-temperature relationships, and signal conditioning techniques. By gaining a deeper insight into the working principles of RTD sensors, engineers can optimize their performance and accuracy in diverse temperature measurement scenarios.
Advantages and Applications of RTD Temperature Sensors
The inherent advantages of RTD temperature sensors make them indispensable for a wide array of industrial and scientific applications. This section will highlight the key advantages of RTD sensors, such as high accuracy, stability, and repeatability, along with their suitability for various temperature measurement tasks. Furthermore, the diverse applications of RTD sensors in industries such as automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and food processing will be explored, showcasing their versatility and reliability in demanding environments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RTD temperature sensors are pivotal instruments for accurate and reliable temperature measurements in industrial and scientific settings. By understanding their functionality, testing methodologies, calibration procedures, wiring and installation techniques, and working principles, professionals can unlock the full potential of RTD sensors for diverse temperature monitoring applications. Leveraging the advantages and applications of RTD sensors enables industries to enhance operational efficiency, quality control, and safety in temperature-sensitive processes.
CTA: For high-quality RTD temperature sensors and expert guidance on their selection and integration, consult with our team of industry professionals. Unlock the potential of precise temperature monitoring in your operations today!