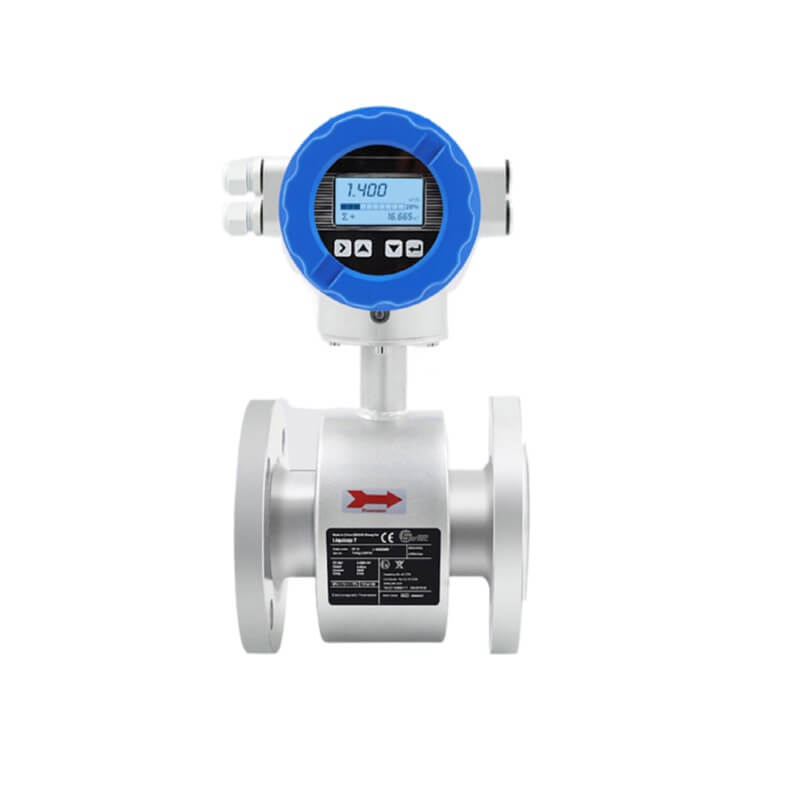
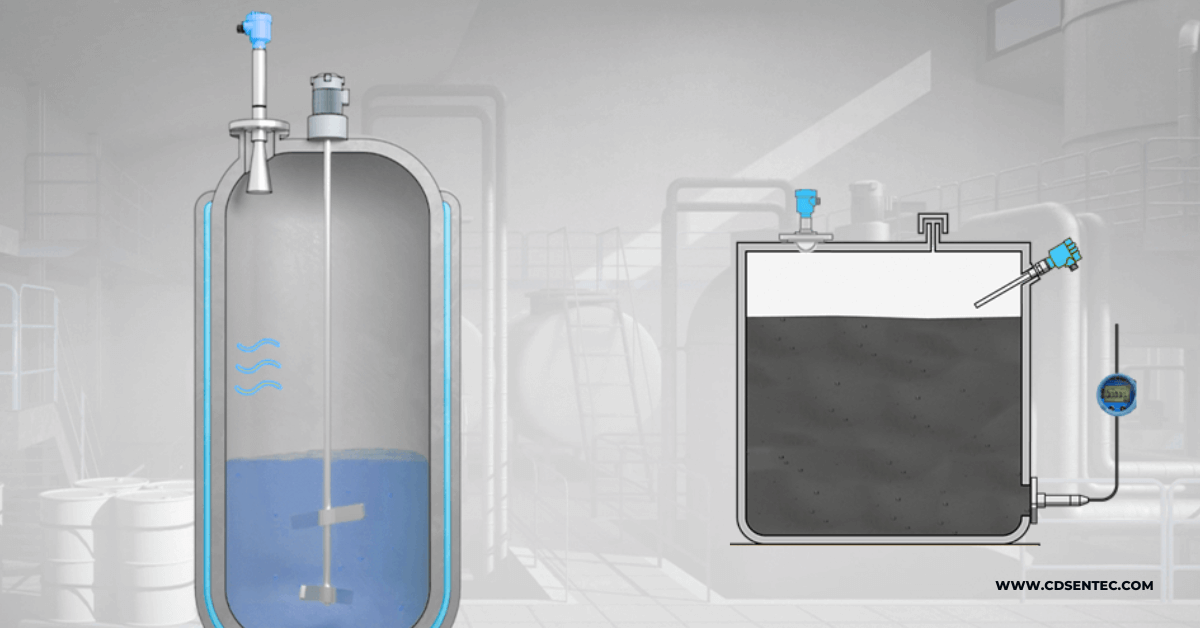
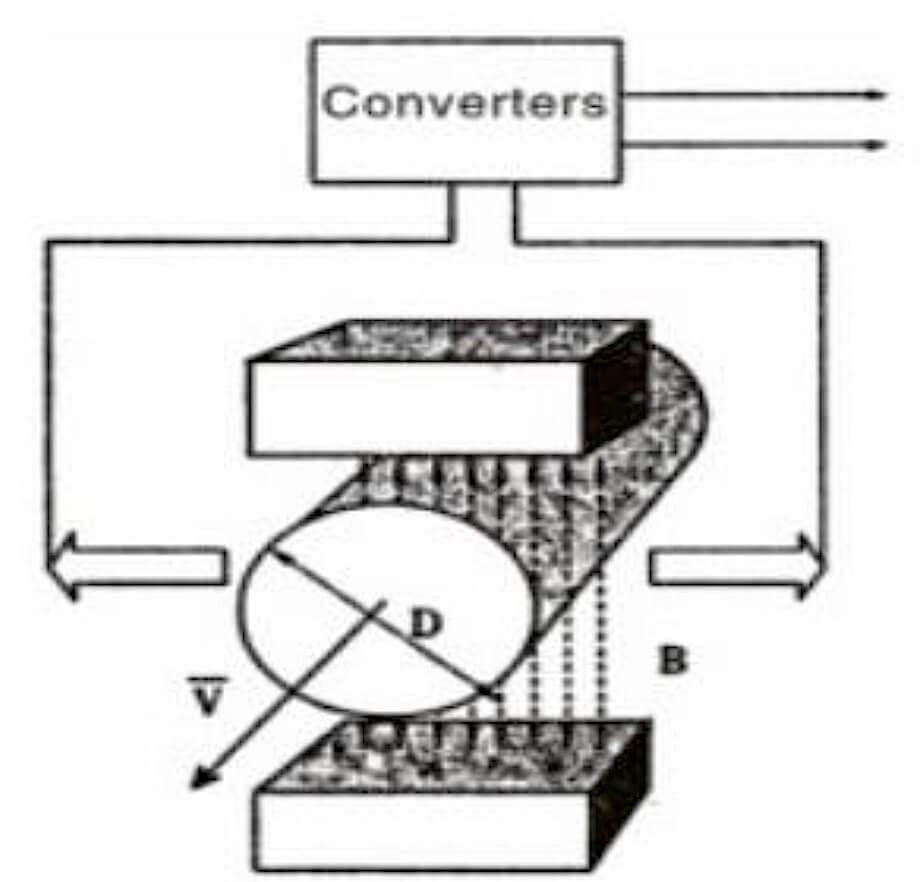
Electromagnetic flowmeter is a kind of flowmeter designed using Ferrari magnetic induction principle. Its main structure is composed of magnetic circuit system, measuring conduit, electrode, shell, lining and converter. This type of flowmeter is very common in the market and is often used in major factories and chemical plants.
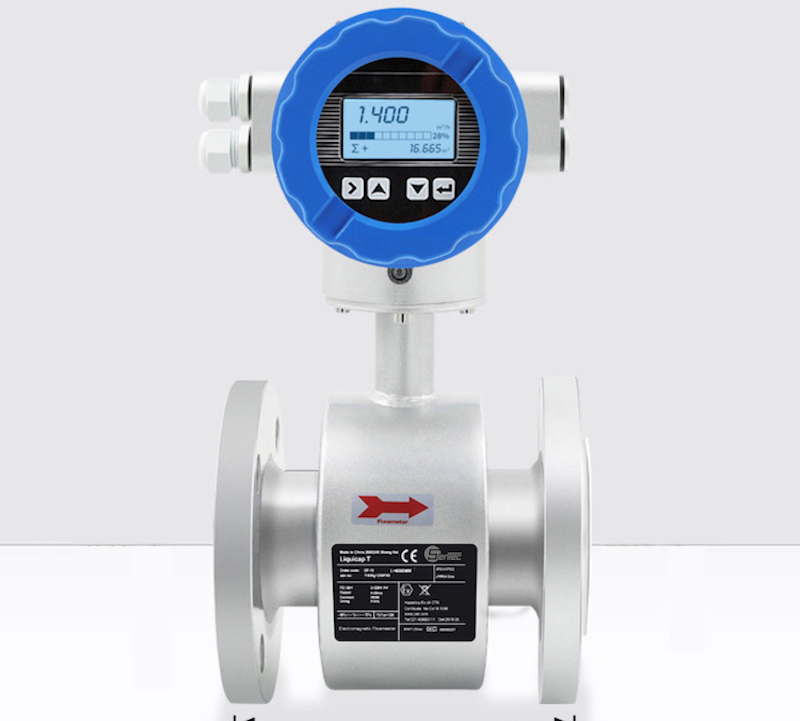

How Electromagnetic Flowmeters Work
Electromagnetic flowmeters operate on the principle of Faraday’s Law of electromagnetic induction. They consist of a flow tube with a magnetic field applied perpendicular to the fluid flow. When a conductive fluid flows through the tube, it generates a voltage proportional to the velocity of the fluid. This voltage is picked up by electrodes positioned on the flow tube walls, and the flow rate can be calculated based on the induced voltage.
Advantages of electromagnetic flowmeters
One of the main advantages of electromagnetic flowmeters is their ability to measure the flow rate of conductive fluids accurately. They can handle a wide range of fluid types, including corrosive and abrasive liquids. Additionally, electromagnetic flowmeters have no moving parts, which means they have a longer lifespan and require minimal maintenance. There are more typical advantages as follows:
1. Electromagnetic flowmeter can be used to measure industrial conductive liquid or slurry.
2. No pressure loss.
3. The measurement range is large, the diameter of the electromagnetic flow transmitter is from 2.5mm to 2.6m, which is more suitable for the field of environmental protection sewage treatment, and the processing speed is faster and faster.
4. The electromagnetic flowmeter measures the volume flow of the fluid to be measured under the working state, and is not affected by the temperature, pressure, density and viscosity of the fluid in the measurement principle.
Disadvantages of electromagnetic flowmeters
1. The application of electromagnetic flowmeter has certain limitations. It can only measure the liquid flow of conductive media, and cannot measure the flow of non-conductive media, such as heating water with better gas and water treatment. In addition, the lining needs to take into account the bearing capacity under high temperature conditions and requires regular maintenance.
2. The electromagnetic flowmeter determines the volume flow in the working state by measuring the speed of the conductive liquid. According to the measurement requirements, for the liquid medium, the mass flow should be measured, and the measured medium flow should involve the density of the fluid. Different fluid media have different densities and change with temperature. If the electromagnetic flowmeter converter does not consider the fluid density, it is inaccurate to only give the volume flow at normal temperature, so it is not suitable for medium detection with temperature changes.
3. The installation and debugging of electromagnetic flowmeters are more complicated and stricter than other flowmeters. The transmitter and the converter must be used together, and two different types of instruments cannot be used between them. When installing the transmitter, from the selection of the installation site to the specific installation and debugging, it must be carried out in strict accordance with the requirements of the product manual. There should be no vibration or strong magnetic field at the installation site. The transmitter and the pipeline must have good contact and good grounding during installation. The potential of the transmitter is equal to that of the fluid being measured. During use, the gas remaining in the measuring tube must be exhausted, otherwise it will cause a large measurement error.
4. When the electromagnetic flowmeter is used to measure the viscous liquid with dirt, the viscous matter or sediment adheres to the inner wall of the measuring tube or the electrode, which makes the output potential of the transmitter change, which brings measurement error, and the dirt on the electrode reaches a certain thickness. , which may cause the meter to fail to measure.
5. If the water supply pipe is fouled, the inner diameter of the pipe becomes smaller, and if the inner diameter of the water supply pipe is worn and the inner diameter of the pipe becomes larger, it will affect the original flow value and cause measurement errors. For example, a 1mm change in the inner diameter of a 100mm instrument will bring about an additional error of about 2%, which will ultimately affect the measurement accuracy.
6. The measurement signal of the transmitter is a small millivolt level potential signal. In addition to the flow signal, there are also some signals unrelated to the flow, such as phase voltage, quadrature voltage and common mode voltage. In order to measure the flow accurately, it is necessary to eliminate various interference signals and effectively amplify the flow signal. The performance of the flow converter should be improved, and it is suitable for the converter of the microprocessor type. It is used to control the excitation voltage, and the excitation mode and frequency are selected according to the properties of the fluid to be measured, which can eliminate in-phase interference and quadrature interference. However, the improved instrument has a complex structure and high cost, so the measurement accuracy will also be affected.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electromagnetic Flowmeter
When selecting an electromagnetic flowmeter, several factors should be taken into consideration:
- Fluid Characteristics: Consider the conductivity, viscosity, and temperature of the fluid to ensure the chosen flowmeter is compatible.
- Pipe Size and Flow Range: Determine the pipe size and the expected flow rate range to select a flowmeter that can accurately measure the desired flow rates.
- Installation Requirements: Consider the space available for installation, as well as any requirements for straight pipe runs or flow conditioning elements.
- Output and Integration: Evaluate the desired output signal and the flowmeter’s compatibility with existing control systems or data acquisition devices.
Common Misconceptions About Electromagnetic Flowmeters
There are a few misconceptions about electromagnetic flowmeters that are worth addressing:
- Limited Applicability to Clean Fluids: While electromagnetic flowmeters are commonly used in dirty fluid applications, they can also accurately measure clean fluids. Their ability to handle a wide range of fluids makes them suitable for various applications.
- Sensitivity to Air Bubbles: Some users believe that air bubbles can affect the accuracy of electromagnetic flowmeters. However, modern flowmeters include features like air bubble detection and compensation algorithms to minimize the impact of bubbles on measurements.
- Inaccuracy with Slurries: Electromagnetic flowmeters can accurately measure slurries with high solid content, provided the solids are conductive. The flowmeter’s accuracy can be affected by the concentration and particle size distribution of the solids.
Comparison with Other Types of Flowmeters
Electromagnetic flowmeters offer several advantages over other flowmeter types:
- Accuracy: Electromagnetic flowmeters provide highly accurate measurements, even for fluids with varying conductivity. They outperform other flow meters, such as turbine or paddlewheel flowmeters, in terms of accuracy.
- Versatility: Unlike some flowmeters that have limitations in terms of fluid compatibility, electromagnetic flowmeters can handle conductive fluids with varying viscosities and corrosiveness.
- Maintenance: Electromagnetic flowmeters have no moving parts, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and ensuring long-term reliability.
Maintenance and Calibration of Electromagnetic Flowmeters
To maintain the accuracy and reliability of electromagnetic flowmeters, regular maintenance and calibration are essential. The following steps are recommended:
- Cleaning and Inspection: Regularly clean the flow tube to remove any buildup or debris that may affect the flowmeter’s performance. Inspect the electrodes for any signs of damage or corrosion.
- Verification and Calibration: Periodically verify the flowmeter’s accuracy by comparing its measurements to a reference standard. If necessary, recalibrate the flowmeter to ensure accurate readings.
- Firmware and Software Updates: Stay up to date with the manufacturer’s firmware and software updates to benefit from new features and improvements.
Conclusion
Electromagnetic flowmeters offer numerous advantages in terms of accuracy, versatility, and maintenance requirements. They are well-suited for measuring the flow rate of conductive fluids in various industries. However, it is important to consider their limitations, such as non-conductive fluid measurement and reduced accuracy at low flow rates. By carefully evaluating the specific application requirements and considering the factors mentioned in this guide, one can select the most suitable electromagnetic flowmeter for their needs. Maintain and calibrate the flowmeter regularly to ensure accurate and reliable measurements over its lifespan.
CTA:
If you are looking for an accurate and versatile flowmeter for your industry needs, contact us today to learn more about our range of electromagnetic flowmeters. Our team of experts will assist you in finding the right solution for your specific requirements.