The differential pressure flow meter is a meter that calculates the flow rate based on the differential pressure generated by the detection part installed in the pipeline, known fluid conditions, and the geometric dimensions of the detection part and the pipeline. The differential pressure flowmeter consists of a standard throttling device, a differential pressure transmitter and a flow totalizer. Differential pressure flowmeters are usually classified in the form of detection parts, such as: orifice flowmeter, venturi flowmeter, averaging velocity tube flowmeter, etc.Differential pressure flow meters can be used to measure the flow rates of most liquids, gases and steam. The accuracy of differential pressure flowmeter measurement depends on the accuracy of the differential pressure transmitter.
What is a differential pressure flow meter?
A differential pressure flow meter is an instrument used to measure the flow of liquids, gases, and steam in a pipe or duct. It operates based on the principle that as fluid flows through a pipe, it creates a pressure drop. This pressure drop is measured by the differential pressure flow meter to determine the flow rate. The meter consists of two pressure sensing elements, one located upstream and the other downstream of a constriction in the pipe. The difference in pressure between the two elements is directly proportional to the flow rate.

Differential pressure flow meters are widely used in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical, water treatment, and HVAC. They offer a cost-effective and reliable solution for flow measurement. These flow meters can handle a wide range of fluid types and are suitable for both high and low flow rates. Additionally, they are easy to install and maintain, making them a popular choice among engineers and technicians.
How is differential pressure related to flow?
The relationship between differential pressure and flow is governed by Bernoulli’s equation, which states that the sum of the pressure, kinetic energy, and potential energy per unit volume of a flowing fluid remains constant along a streamline. In the context of a differential pressure flow meter, the pressure drop across the constriction in the pipe is directly proportional to the square of the flow rate.
This relationship is established by the use of the Venturi effect, where the fluid accelerates as it passes through the constriction, causing a decrease in pressure. The pressure drop is then measured by the differential pressure flow meter and converted into a flow rate using a calibration factor. By accurately measuring the differential pressure, the flow meter provides valuable data for process control, monitoring, and optimization.
When the fluid flows through the throttle, the fluid will be accelerated due to the compression of the fluid, and the kinetic energy of the fluid will increase correspondingly due to the increase in the velocity of the fluid. According to the law of conservation of energy, we know that the static pressure of the fluid at the accelerated point will decrease accordingly numerical value.
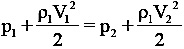
How accurate is a DP flowmeter?
Differential pressure flow meters are known for their high accuracy and reliability. The accuracy of a DP flow meter depends on various factors including the design, calibration, and installation. Typically, these flow meters have an accuracy of ±1% to ±3% of the measured flow rate. However, with proper calibration and regular maintenance, this accuracy can be further improved.
To ensure the accuracy of a DP flow meter, it is important to consider factors such as the fluid properties, pipe size, and flow profile. The fluid properties, such as viscosity and density, can affect the pressure drop and flow measurement. The pipe size should be appropriate to minimize turbulence and pressure losses. Additionally, the flow profile should be uniform to obtain accurate readings. By considering these factors and following best practices, the accuracy of a DP flow meter can be optimized for specific applications.
Advantages of differential pressure flow meters
a. It has a wide range of applications. So far there is no other type of flowmeter comparable to a differential pressure flowmeter.
b. The orifice plate is the most widely used differential pressure flow meter. It has a firm structure, stable and reliable performance and long service life.
c. The detection parts, differential pressure transmitter, and flow totalizer can be produced by different manufacturers, which is convenient for scale economic production
Disadvantages of differential pressure flowmeter
The measurement accuracy of differential pressure flow meters is generally low.
High requirements for on-site installation conditions of differential pressure flowmeters.
The range is narrow, generally only 3:1-4:1
The pressure loss of orifice plate and nozzle is large.
Throttle device series
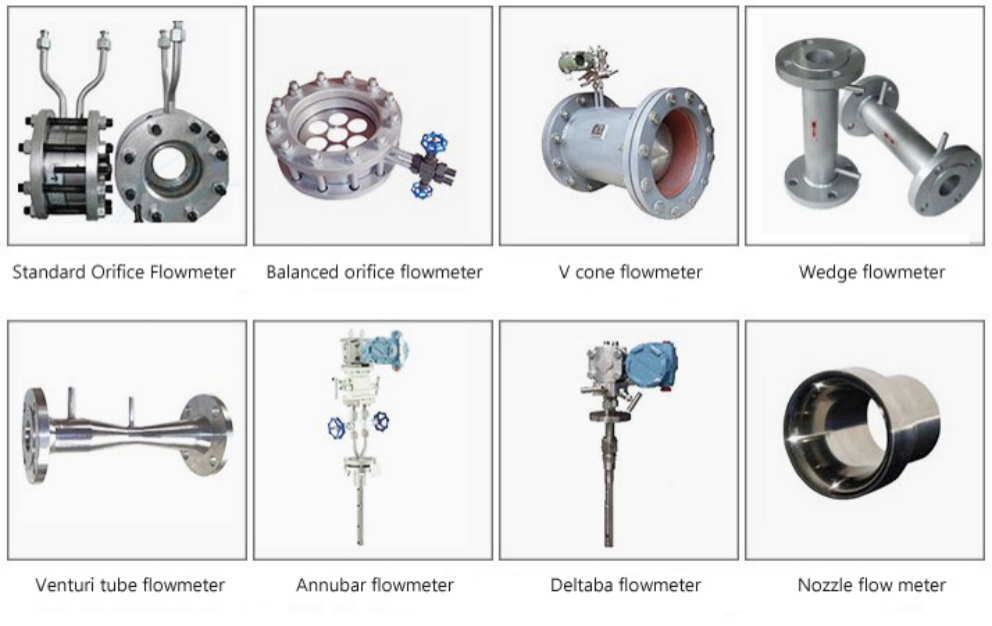

Features of throttling device
Standard orifice plate: It has the characteristics of high measurement accuracy, convenient installation, wide range of use, and low cost. It is widely used in flow measurement of various media.
Ring-shaped orifice plate, round orifice plate, eccentric orifice plate: It is not easy to be blocked, and the front and rear straight pipes are short. It is suitable for the measurement of gas and liquid containing dust and impurities such as blast furnace gas and coke oven gas.
Standard nozzle: It has the characteristics of high temperature and pressure resistance, impact resistance, long service life, large measurement range and high measurement accuracy. It is suitable for the measurement of high temperature and high pressure steam flow in power plants, heating network pipelines, and fluid flow with high velocity. There are two forms: A: ISA1932 nozzle (standard nozzle) B: long diameter nozzle
Classic Venturi tube/Venturi nozzle: It has the characteristics of small pressure loss, high measurement accuracy, short front and rear straight tubes, and long service life. Suitable for flow measurement of water and gas.
Types of differential pressure flow meters
There are several types of differential pressure flow meters available, each with its own advantages and limitations. The most commonly used types include orifice plate, venturi tube, and flow nozzle.
- Orifice plate: This is the simplest and most economical type of DP flow meter. It consists of a flat plate with a hole (orifice) in the center, which creates a pressure drop when fluid flows through it. Orifice plates are versatile and can be used for a wide range of flow rates and fluid types. However, they can cause significant pressure losses and are less accurate compared to other types.
- Venturi tube: The Venturi tube is a more advanced type of DP flow meter that provides better accuracy and lower pressure losses compared to orifice plates. It has a converging section followed by a throat and a diverging section. This design allows for better flow profile and reduced turbulence, resulting in improved accuracy. Venturi tubes are commonly used in applications where high accuracy is required.
- Flow nozzle: Flow nozzles are similar to venturi tubes but have a different shape. They have a rounded entrance followed by a throat and a straight outlet section. Flow nozzles offer better accuracy and higher flow capacity compared to orifice plates. They are commonly used in high-pressure and high-velocity applications.
Factors to consider when selecting a differential pressure flow meter
The selection of differential pressure flowmeter should consider the following aspects:
Accuracy, repeatability, linearity, flow range and range The standard parts of the differential pressure flowmeter have a strict range of use, including parameters such as pipe diameter ratio, Reynolds coefficient, pipe wall thickness, etc. Therefore, these series of parameters should be selected reasonably in actual selection and application. In addition, the accuracy of the differential pressure flowmeter depends to a large extent on the use conditions of the site, and generally depends on the fluid conditions.
Fluid characteristics: The characteristics of the fluid refer to the fluid’s medium conditions such as density, dynamic viscosity, pressure, temperature, corrosivity, abrasion, fouling, and dirt. Therefore, when choosing a differential pressure flowmeter that should be reasonably selected according to the physical characteristics of the fluid medium on site, the instrument should be used to measure these physical parameters without understanding the physical characteristics of the fluid on site.
Economic factors: Should consider the purchase cost, installation cost, maintenance cost and calibration cost of the differential pressure flowmeter after installation. The later operating cost of a larger diameter differential pressure flowmeter is a relatively large expense, so you should choose a suitable diameter differential pressure flowmeter when selecting the model.
Pressure loss: Large pressure loss is one of the main disadvantages of differential pressure flow meters. In various throttling devices, the orifice plate and nozzle are the throttling parts with large pressure loss. At the same flow rate and β value, the pressure loss of the nozzle is only 30%-50% of the pressure loss of the orifice plate, which means that the nozzle is Lower pressure loss. Various flow tubes (Venturi tube, Dole tube, Rollos tube, General Venturi tube, etc.) are throttling devices with low pressure loss. Their pressure loss is only 20% of the orifice, or even as low as 5%-10 %. The development and application of these throttling devices is a direction for future efforts
Applications of differential pressure flow meters
Differential pressure flow meters find applications in a wide range of industries and processes. Some common applications include:
- Oil and gas: DP flow meters are used to measure the flow of oil, gas, and other fluids in pipelines, refineries, and offshore platforms. They provide valuable data for production monitoring, custody transfer, and process optimization.
- Chemical industry: These flow meters are widely used in chemical plants for measuring the flow of various chemicals and solvents. They ensure accurate dosing, batch control, and inventory management.
- Water treatment: DP flow meters are essential for monitoring and controlling the flow of water in treatment plants, distribution networks, and wastewater systems. They help in optimizing the treatment process and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
- HVAC systems: Differential pressure flow meters play a crucial role in HVAC systems for measuring the flow of air and gases. They help in maintaining proper ventilation, balancing air distribution, and optimizing energy consumption.
- Pharmaceutical industry: These flow meters are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to ensure precise flow control and accurate dosing of liquids and gases.
Comparison with other types of flow meters
While differential pressure flow meters are widely used and offer several advantages, it is important to understand their limitations and compare them with other types of flow meters. Some common alternatives to DP flow meters include:
- Magnetic flow meters: Magnetic flow meters use Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction to measure the flow of conductive fluids. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, including corrosive and abrasive fluids. Magnetic flow meters do not have any moving parts, making them highly reliable and low maintenance. However, they are not suitable for non-conductive fluids and have limitations in low flow rate applications.
- Ultrasonic flow meters: Ultrasonic flow meters use ultrasound waves to measure the velocity of the fluid flow. They are non-intrusive, easy to install, and can measure a wide range of flow rates. Ultrasonic flow meters are suitable for both liquid and gas applications. However, they may be affected by factors such as temperature, pipe material, and fluid properties. They also tend to be more expensive compared to differential pressure flow meters.
- Coriolis flow meters: Coriolis flow meters measure the mass flow rate of fluids by detecting the Coriolis force generated when the fluid flows through a vibrating tube. They offer high accuracy and can measure both mass flow rate and density. Coriolis flow meters are suitable for a wide range of fluid types, including viscous and multiphase fluids. However, they can be expensive and require regular calibration.
The choice between differential pressure flow meters and other types of flow meters depends on the specific application requirements, fluid properties, accuracy needs, and budget constraints. Consulting with flow measurement experts and conducting a thorough evaluation can help in selecting the most suitable flow meter for a given application.
Conclusion
Differential pressure flow meters are versatile and reliable instruments used for measuring the flow of fluids and gases in a wide range of applications. They provide accurate and cost-effective solutions for flow measurement and control. Understanding the principles, types, and applications of differential pressure flow meters is crucial for selecting the most suitable meter for a specific application. By considering factors such as flow range, fluid properties, accuracy requirements, and installation considerations, engineers and technicians can make informed decisions and ensure accurate flow measurement. Consulting with flow measurement experts can further enhance the selection process and optimize the performance of differential pressure flow meters.
CTA:
To learn more about differential pressure flow meters and their applications, contact our flow measurement experts today. We offer comprehensive solutions tailored to your specific needs.




