Hvac sensor solutions and applications
HVAC sensor solutions and applications play a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable indoor climate and optimizing the performance of HVAC systems. These sensors are designed to monitor various parameters such as pressure, temperature, humidity, and vibration. By continuously collecting data on these parameters, the sensors enable diagnostics that can help identify system or equipment issues, reducing inefficiencies and preventing major breakdowns.
Table of Contents
Backgroud: building HVAC control system
A building HVAC control system is a sophisticated network of sensors, controllers, and actuators that work together to regulate and optimize the heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems in a building. A building HVAC control system is a vital component of modern building construction industry, ensuring optimal comfort, energy efficiency, and sustainability. It integrates sensors, controllers, actuators, and a centralized BAS to monitor and regulate the HVAC system, providing real-time data, predictive maintenance, and remote control capabilities. By implementing a robust control system, building owners can create a comfortable and healthy indoor environment while minimizing energy consumption and operational costs.
Sensors for HVAC Applications & Solutions
Sensors for HVAC applications are essential components that enable the monitoring and control of various parameters within a heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system. These sensors provide real-time data to optimize system performance, improve energy efficiency, and ensure a comfortable indoor environment. Here are some common types of sensors used in HVAC applications:
Temperature Sensors: Temperature sensors are widely used in HVAC systems to measure and control the temperature of the air or fluid flowing through the system. They provide feedback for adjusting heating and cooling operations, maintaining the desired temperature setpoints, and preventing overheating or overcooling.
Humidity Sensors: Humidity sensors measure the moisture content in the air and help regulate humidity levels within a space. They ensure optimal humidity conditions for comfort, prevent the growth of mold and mildew, and protect sensitive equipment from moisture damage.
Pressure Sensors: Pressure sensors are employed to measure air pressure within ducts, pipes, or HVAC equipment. They help monitor and control airflow, ensuring that air is properly distributed throughout the system. Pressure sensors also aid in identifying abnormalities, such as leaks or blockages.
Occupancy Sensors: Occupancy sensors detect the presence or absence of people in a room or zone. They help optimize energy usage by adjusting HVAC settings based on occupancy. For example, when a room is unoccupied, the HVAC system can be set to energy-saving mode, reducing unnecessary cooling or heating.
CO2 Sensors: Carbon dioxide (CO2) sensors are used to monitor indoor air quality (IAQ). High CO2 levels can indicate poor ventilation, leading to discomfort and health issues. These sensors provide feedback to adjust ventilation rates and ensure fresh air circulation for a healthier indoor environment.
Vibration Sensors: Vibration sensors detect abnormal vibration levels in HVAC equipment. By monitoring vibrations, these sensors help identify potential mechanical issues or failing components, enabling timely maintenance or repairs to prevent system breakdowns.
Air Quality Sensors: Air quality sensors measure various pollutants, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, and gases like carbon monoxide (CO). These sensors provide crucial data for monitoring and improving IAQ, ensuring a healthy and safe indoor environment.
In addition to these sensors, advanced HVAC systems may also incorporate smart thermostats or building automation systems that integrate multiple sensors and enable centralized control and monitoring of the entire HVAC system.
Overall, sensors for HVAC applications play a vital role in optimizing system performance, enhancing energy efficiency, and creating a comfortable and healthy indoor environment. By providing real-time data and facilitating intelligent control, these sensors enable proactive maintenance, reduce energy waste, and improve occupant comfort and well-being.
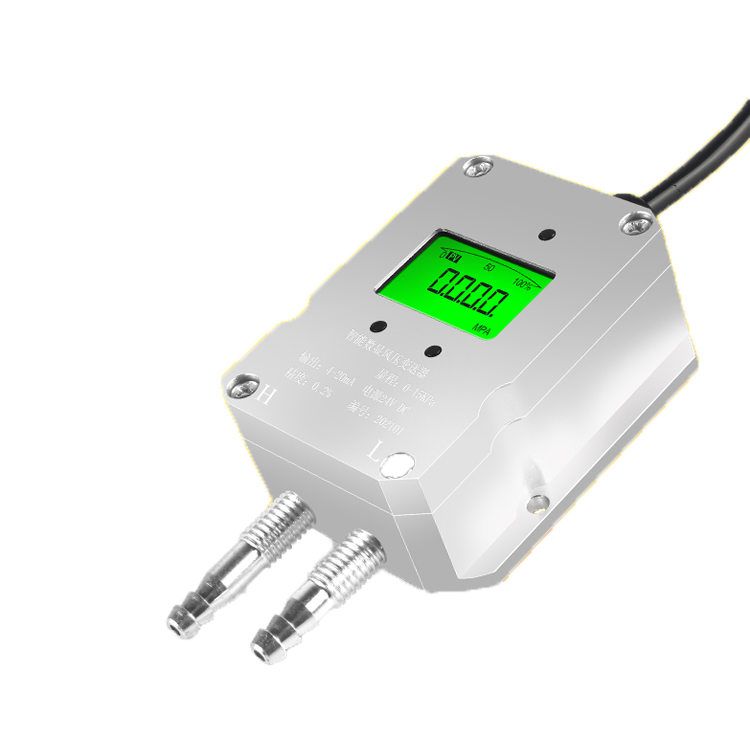
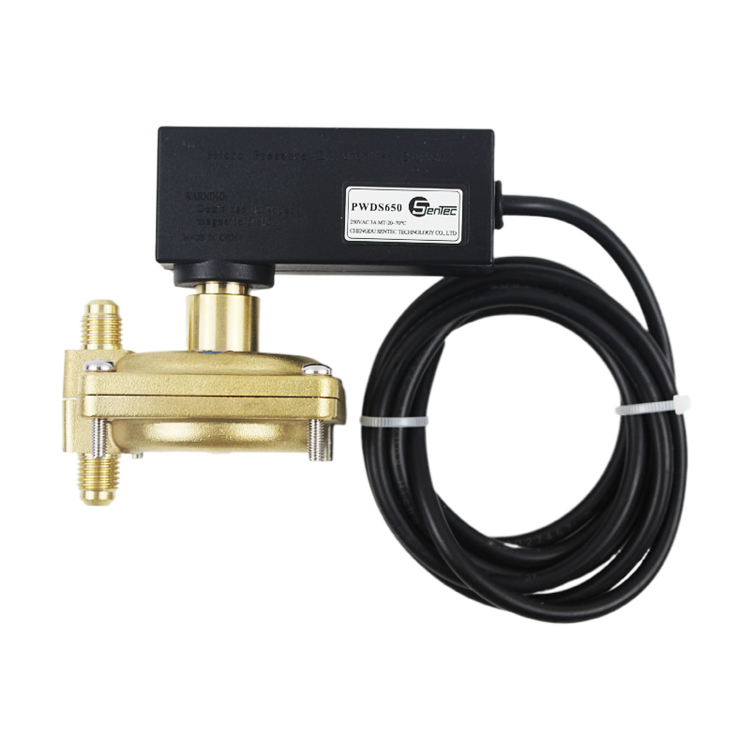
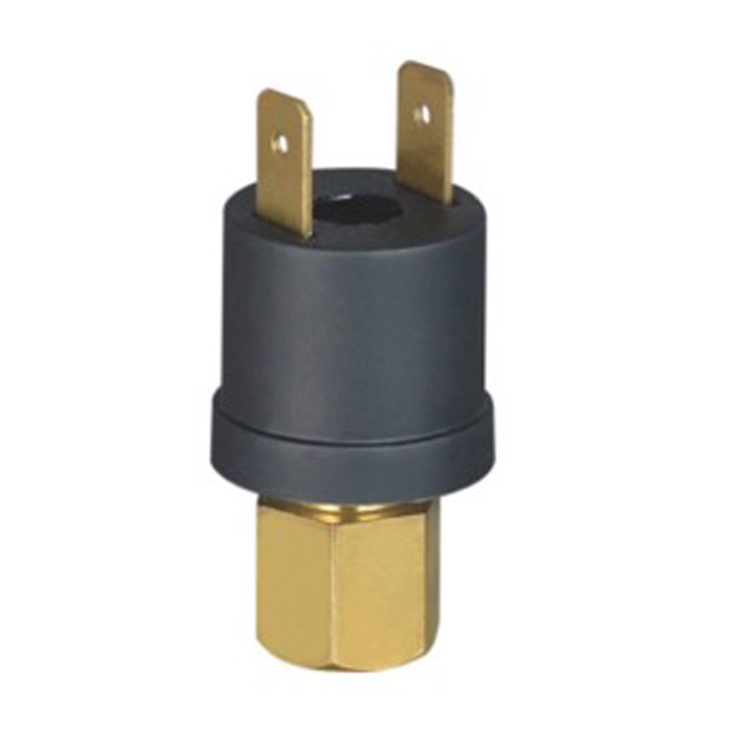
HVAC Applications & Solutions: HAVC pressure sensor
A pressure sensor is an essential component in an HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system. It measures the pressure of the refrigerant or air within the system and provides crucial data for maintaining optimal system performance.
HVAC pressure sensors function is to monitor the pressure levels in various parts of the system, such as the condenser, evaporator, and refrigerant lines. They help ensure that the system operates within the desired pressure range, preventing damage to components and ensuring efficient operation.
HVAC pressure sensors types includes differential pressure sensors, absolute pressure sensors, and gauge pressure sensors. Each type is designed to measure pressure in specific applications within the HVAC system.
HVAC pressure sensors are typically connected to the building automation system (BAS) or HVAC control system. This integration allows for centralized monitoring and control of the system, enabling proactive maintenance, fault detection, and diagnostics.
In summary, HVAC pressure sensors play a vital role in maintaining optimal system performance, energy efficiency, and safety. They provide real-time pressure data, facilitate intelligent control, and contribute to the overall comfort, efficiency, and sustainability of HVAC systems in modern buildings.
HVAC Applications & Solutions: HAVC Air Quality sensor
Air quality sensors are essential in manufacturing and industrial facilities. Many commercial buildings today are equipped with these sensors to improve the efficacy and efficiency of air purifiers and HVAC. Air quality sensors are also necessary for health and safety. Smart Air Quality Sensors can detect the following according to specifications: carbohydrate combustible gas dust, hydrogen, hydrogen sulfide, methane, nitrous oxide, nitric oxide, nitrous oxide, oxygen, ozone, particulate matter, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds . Industrial facilities and commercial establishments dealing with hazardous materials require air quality detectors to cover these fumes, gases or volatile compounds.
In addition, air quality sensors have a specific detection sensitivity. Residential and public buildings require sensitive air quality sensors. Otherwise, any low levels of harmful gases, particulates and volatile organic compounds may remain undetectable. IoT building management systems must connect such smart air quality sensors to a central infrastructure and control interface. Properties also need a sufficient number of air quality sensors, such as HVAC and purifier areas.
Subscribe To get new products and solutions
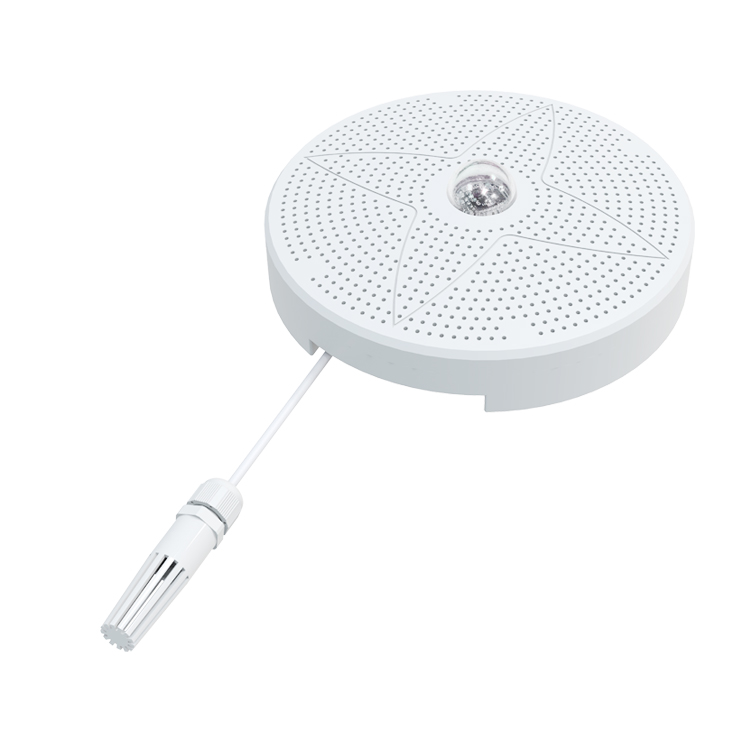
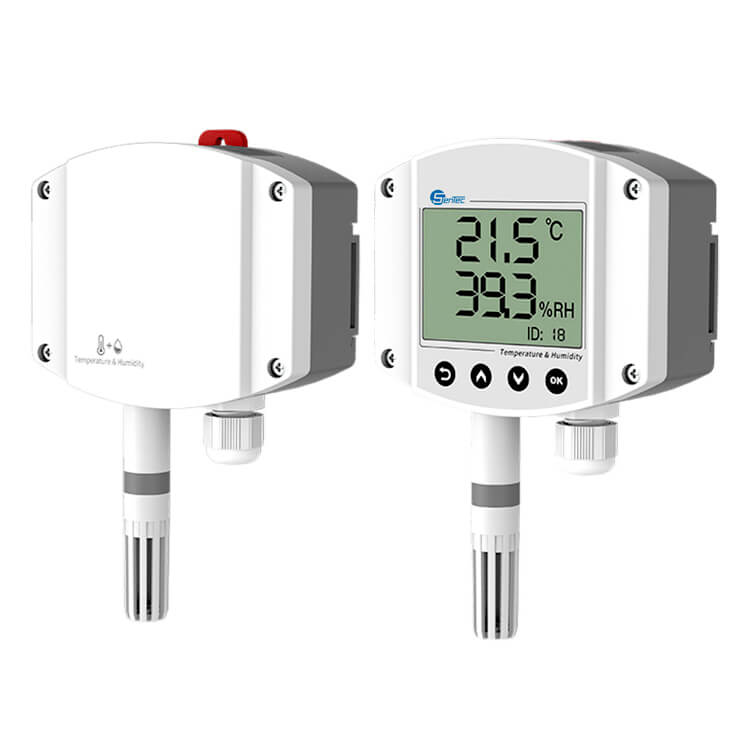
HVAC Applications & Solutions: HVAC Temperature Humidity sensor
Most residential, commercial, and industrial properties require multiple temperature and humidity sensors, depending on the number of HVAC zones in the building. Thus, temperature sensors can control heating, cooling and ventilation in each zone, typically with an accuracy of +/- 1 degree.
While hygrometers only measure relative humidity in the air or inside a building, smart sensors go a step further and regulate ambient humidity.
1) Capacitive humidity sensors are suitable for residential and commercial buildings. Capacitive hygrostats are used in most HVAC systems, refrigerators, ovens, and automobiles.
2) Resistive humidity sensors are not as accurate as capacitive hygrostats. However, resistive hygrostats are more affordable and therefore the first choice for larger properties.
Latest Posts

Why Your Thermocouple Calibration Might Be Wrong (And How to Fix It)

Why Engineers Choose Radar Level Measurement for Bypass Installations

TVOC Air Quality Testing: Essential Facts for a Healthier Indoor Environment