Introduction
A Integrated temperature and pressure sensor combines temperature and pressure measurement into a single device, offering several advantages for industrial applications. By simultaneously monitoring both parameters, it provides more accurate and reliable data, which is essential for processes where temperature and pressure are interdependent, such as in chemical reactions, fluid dynamics, or gas flow monitoring. This integration reduces the need for multiple sensors, simplifying installation, minimizing wiring, and lowering overall system costs. Additionally, having a single device improves data synchronization, reducing measurement discrepancies caused by sensor placement variations. The compact design also saves space, making it ideal for applications with limited installation ro-om. Overall, thermo-pressure integrated sensors enhance efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in various industrial settings.
This article examines three SenTec’s common structural designs of integrated temperature and pressure transmitters, analyzing their advantages, disadvantages, and ideal application scenarios.
Overview of Sensor Structures
Currently, Sentec’s three main structural designs distinguish integrated temperature and pressure sensors based on their housing and sensor arrangement:
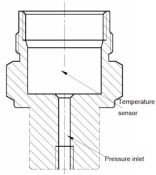
Type 1: Fully Integrated Signal Collection
Structure:
- The temperature and pressure sensing elements are fully integrated within a single unit.
- A compact and unified design facilitates easy assembly and installation.
Advantages:
- Simple assembly, making mass production more convenient.
- Lower production costs due to reduced components and manufacturing steps.
- Suitable for general industrial applications where precision is not the primary concern.
Disadvantages:
- Temperature measurement accuracy is relatively low.
- Thermal interference between pressure and temperature sensors can result in a 2–4°C measurement error.
Best Use Cases:
- General industrial applications where moderate temperature measurement accuracy is acceptable.
- HVAC systems for monitoring fluid pressure and temperature.
- Water treatment plants for basic process control.
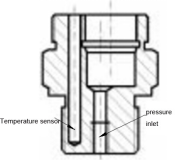
Type 2: Independent Signal Collection with Embedded Temperature Probe
Structure:
- The temperature sensor is embedded inside the housing for protection.
- Temperature and pressure sensors operate independently, reducing signal interference.
Advantages:
- Better temperature accuracy than Type 1, with 2–3°C measurement error.
- The embedded temperature probe enhances sensor durability by protecting it from external impacts.
- Independent operation of the two sensors ensures more stable readings.
Disadvantages:
- Larger housing size increases material costs.
- Installation options are limited due to the larger thread and mounting requirements.
Best Use Cases:
- Chemical processing plants requiring improved measurement stability.
- Oil and gas pipelines where durability is crucial.
- Food and beverage industry for pasteurization and sterilization processes.
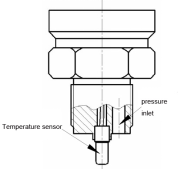
Type 3: Independent Signal Collection with Direct Media Contact
Structure:
- The temperature probe is directly exposed to the medium for more accurate temperature sensing.
- Independent measurement ensures high precision.
Advantages:
- Highest temperature accuracy, with a 1–3°C measurement error.
- Direct contact with the medium allows for fast response times in dynamic conditions.
- Suitable for critical applications where precise temperature control is essential.
Disadvantages:
- The exposed temperature probe is more vulnerable to damage.
- Larger housing size and complex manufacturing increase production costs.
- Installation can be challenging in space-constrained environments.
Best Use Cases:
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing for precise process control.
- Power plants and steam systems, where rapid temperature changes must be monitored accurately.
- Aerospace and automotive applications, where precise fluid temperature measurement is critical.
Conclusion
Choosing the right integrated temperature and pressure sensor depends on the accuracy requirements, environmental conditions, and durability needs of the application.
- Type 1 is best for general industrial use where moderate accuracy is acceptable.
- Type 2 provides a balance between protection and accuracy, making it ideal for harsh environments.
- Type 3 offers the highest precision and fast response times, suitable for critical industries.
Pressure and temperature integrated transmitter is widely used in various pressure measurement due to its excellent accuracy and reliability. Especially in coal mine, oil field, chemical industry, civil explosion, environmental protection, medicine, water affairs, shipping and other industries.
Sentec can customize all three types of temperature-pressure sensors according to the specific needs of the customer, offering tailored solutions for diverse industrial applications.





