In the modern industrial era, the importance of process control instrumentation cannot be overstated. It’s the lifeline of any manufacturing process, providing accurate, real-time data for monitoring and control. Process control instrumentation is a complex system of sensors, transmitters, controllers, and other devices designed to measure and control physical quantities such as temperature, pressure, flow, and level in an industrial process.
In the realm of cement plants, process control instrumentation is the key to achieving high-quality cement and efficient production. It ensures that all operations, from the raw material preparation to the final cement grinding, are executed with precision and reliability. Without process control instrumentation, it would be nearly impossible to maintain consistent quality and efficient operations in a cement plant.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of mastering process control instrumentation in cement plants. It highlights the importance of instrumentation in cement industries, the role of monitoring control systems, the various types of instrumentation used, and how to implement a control and instrumentation system for optimal results.
Importance of Instrumentation in Cement Industries
Instrumentation in Cement Industries plays a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth operation of the entire manufacturing process. It enables precise measurement and control of the physical and chemical parameters of the raw materials and the final product. This precision is crucial to maintain the quality of the cement and to ensure the efficiency of the production process.
Instrumentation in cement industries also ensures safety by monitoring critical parameters that could lead to hazardous situations if not controlled properly. For example, it helps control the temperature in the kiln, thereby preventing overheating that could potentially lead to fires or explosions.
Moreover, cement plants operate under stringent environmental regulations. Instrumentation plays a significant role in monitoring and controlling the emissions from the plant, ensuring compliance with these regulations. Thus, it is evident that the role of instrumentation in cement industries extends beyond just production and quality control. It is instrumental in ensuring safety and environmental compliance as well.
Understanding Monitoring Control Systems for Cement Plants
Monitoring control systems for cement plants are the heart of process control instrumentation. They provide the necessary interface between the operators and the process, enabling efficient control and management of the entire production process.
The primary function of these systems is to continuously monitor the various parameters of the process, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and chemical composition. The data gathered by the sensors is transmitted to the control room, where it is analysed and processed. Based on this analysis, the control system generates control signals that adjust the operation of the equipment to maintain the desired conditions.
Monitoring control systems for cement plants are also responsible for alarm management. They alert the operators in case any parameter deviates from the set limits, allowing for timely intervention and preventing potential mishaps.
Moreover, these systems provide historical data that can be used for trend analysis, process optimization, and predictive maintenance. They also integrate with other systems in the plant, such as the manufacturing execution system (MES) and the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, ensuring seamless information flow and efficient decision-making.
Detailed Overview of Systems and Solutions Used in Cement Plants
The systems and solutions used in cement plants are varied and complex. They include raw material handling systems, grinding systems, pyro-processing systems, cement grinding systems, and packing systems. Each of these systems requires a dedicated set of process control instruments to ensure efficient operation and quality control.
Raw material handling systems, for instance, require level sensors to monitor the level of raw materials in the storage silos and belt weigh feeders to measure the quantity of raw materials being fed into the grinding system. Similarly, the grinding system requires pressure and temperature sensors to monitor the conditions inside the mill, and particle size analyzers to measure the fineness of the ground material.
The pyro-processing system, which is the heart of the cement plant, requires a comprehensive set of instruments. These include temperature and pressure sensors for the preheater and the kiln, gas analyzers to monitor the composition of the kiln gas, and mass flow meters to measure the flow of materials through the system.
The cement grinding and packing systems also require specialized instruments for quality control and efficient operation. For example, the cement grinding system requires particle size analyzers to control the fineness of the cement, and the packing system requires weight sensors to ensure accurate packing of the cement bags.
Types of Instrumentation for Cement Plants
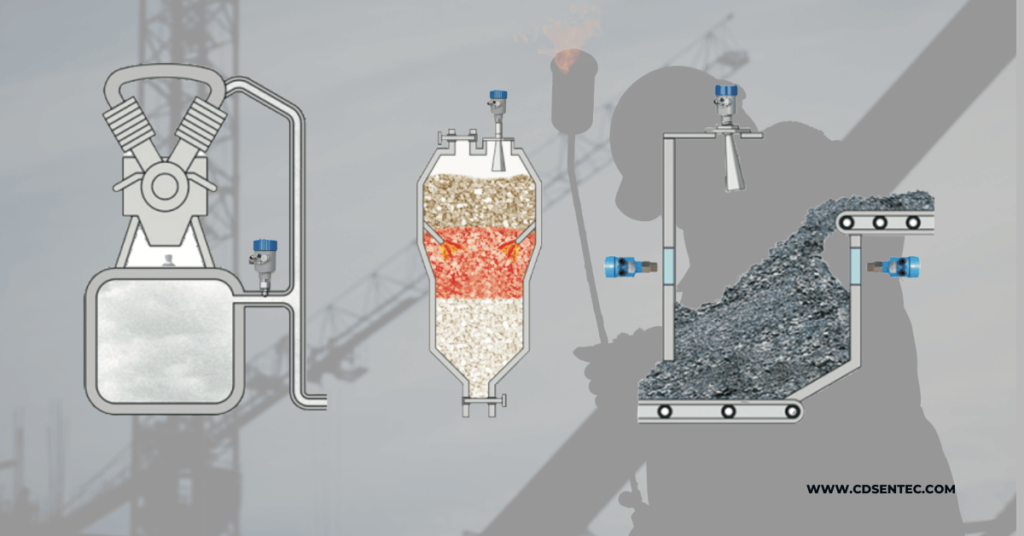
The types of instrumentation for cement plants can be broadly classified into measurement instruments and control instruments. Measurement instruments are devices that measure physical or chemical parameters, such as temperature, pressure, flow, level, and chemical composition. They include sensors, transducers, and analyzers.
Control instruments, on the other hand, are devices that control the operation of the process equipment based on the data received from the measurement instruments. They include controllers, actuators, and control valves.
In the context of a cement plant, typical measurement instruments include temperature sensors for the kiln and the coolers, pressure sensors for the grinding mills and the separators, flow meters for the raw material and the clinker flow, level sensors for the silos, and gas analyzers for the kiln and the stack.
Control instruments in a cement plant typically include PID controllers for the kiln and the mills, control valves for the raw mill and the cooler, and actuators for the feeders and the separators.
Role of Control and Instrumentation System in Cement Industry
The role of the control and instrumentation system in the cement industry extends beyond just measurement and control. It is instrumental in optimizing the process, improving energy efficiency, reducing downtime, and ensuring safety.
Process optimization involves adjusting the operation of the process to achieve the desired output at the lowest cost. The control and instrumentation system plays a crucial role in this by providing real-time data that can be used to identify inefficiencies and take corrective action. For example, it can help adjust the raw mix composition to reduce the clinker factor, thereby reducing the energy consumption and the CO2 emissions.
The control and instrumentation system also helps reduce downtime by providing diagnostic information that can be used for preventive maintenance. For example, it can help identify wear and tear in the grinding media, enabling timely replacement and preventing unplanned shutdowns.
Safety is another important aspect where the control and instrumentation system plays a key role. It helps monitor critical parameters that could lead to hazardous situations, such as overheating of the kiln or excessive pressure in the grinding mill. By alerting the operators in time, it helps prevent accidents and ensure the safety of the personnel and the equipment.
An Insight into Process Control Instruments Used in Cement Processing
Process control instruments used in cement processing are designed to handle the harsh conditions prevalent in a cement plant. They need to be robust, reliable, and accurate, as any deviation in the measurements can lead to significant quality issues and operational inefficiencies.
Temperature sensors, for example, need to withstand the high temperatures in the kiln and the coolers, which can exceed 1000°C. They also need to be resistant to aggressive gases and dust, which are common in a cement plant.
Pressure sensors used in the grinding mills and the separators need to be highly accurate, as even a small variation in the pressure can affect the efficiency of the grinding process and the quality of the cement.
In cement plants, bulk material level measurements are crucial for efficient and safe operations. Several measurement procedures and devices are used to ensure accurate and reliable results. SenTec, a global manufacturer of level sensors, provides robust and maintenance-free sensors specifically designed for the cement industry. These sensors are able to withstand harsh operating conditions and can be customized to fit different measuring tasks. They offer instruments for display, adjustment, and connection, including wireless technology.
Flow meters used to measure the flow of raw materials and clinker need to be capable of handling the abrasive nature of these materials. They also need to be insensitive to variations in the material properties, such as density and viscosity.
Gas analyzers used in the kiln and the stack need to be capable of measuring a wide range of gases, including CO2, NOx, SOx, and CO. They also need to be resistant to high temperatures and aggressive gases.
Importance of Cement Plant Monitoring for Efficient Production
Cement plant monitoring is essential for efficient production. It provides real-time data on the performance of the process, allowing for timely intervention and corrective action. Without proper monitoring, inefficiencies could go unnoticed, leading to increased energy consumption, reduced output, and poor quality cement.
Monitoring also helps identify trends in the process performance. For example, a gradual increase in the kiln temperature could indicate a buildup of coating inside the kiln, requiring corrective action. Similarly, a gradual decrease in the mill output could indicate wear and tear of the grinding media, requiring replacement.
Monitoring also enables preventive maintenance, which can significantly reduce downtime. By identifying potential issues before they become critical, it allows for planned maintenance, reducing the risk of unplanned shutdowns.
Moreover, monitoring helps ensure compliance with environmental regulations. By continuously monitoring the emissions from the plant, it ensures that the plant operates within the permissible limits, preventing potential penalties and reputational damage.
An Exploration of Process Control Solutions for Cement Plants
Process control solutions for cement plants are designed to provide comprehensive control and monitoring of the entire production process. They integrate the various process control instruments and the operational data into a unified system, providing a holistic view of the plant performance.
These solutions typically include a distributed control system (DCS) that provides centralized control of the entire plant. The DCS interfaces with the various process control instruments, collecting data, generating control signals, and providing visualisation and reporting tools for the operators.
Advanced process control (APC) solutions are another important component of process control solutions for cement plants. APC uses mathematical models of the process to predict the process behavior and generate optimal control strategies. This allows for tighter control of the process, leading to improved quality, reduced energy consumption, and increased throughput.
Other components of process control solutions for cement plants include asset management systems (AMS) that provide diagnostic information for preventive maintenance, and manufacturing execution systems (MES) that integrate the operational data with the business data, providing insights for strategic decision-making.
Implementing Control and Instrumentation System for Cement Plants
Implementing a control and instrumentation system for cement plants involves several steps. The first step is to perform a detailed analysis of the process to identify the critical parameters that need to be controlled and monitored. This typically involves consultation with process experts and a review of the process flow diagrams and the equipment specifications.
The next step is to select the appropriate process control instruments for the identified parameters. This involves evaluating the technical specifications of the instruments, their suitability for the process conditions, and their compatibility with the existing infrastructure.
Once the instruments are selected, they need to be installed and commissioned. This involves calibrating the instruments, configuring the control loops, and testing the system to ensure it operates as expected.
After the system is operational, it needs to be maintained regularly to ensure it continues to operate optimally. This involves routine calibration of the instruments, preventive maintenance of the equipment, and periodic review of the system performance.
Mastering Process Control for the Cement Industry
Mastering process control for the cement industry involves a deep understanding of the process, the control principles, and the operation of the process control instruments. It requires a systematic approach to problem-solving, a keen eye for detail, and a strong commitment to continuous learning and improvement.
Process control experts in the cement industry need to be well-versed with the process flow, the chemical reactions, and the physical transformations that occur in a cement plant. They need to understand the interdependencies between the various process parameters and how they affect the quality of the cement and the efficiency of the production process.
They also need to have a thorough understanding of control theory, including concepts like feedback control, feed-forward control, PID control, and model predictive control. They need to understand how to tune the control loops for optimal performance and how to troubleshoot control issues.
Lastly, they need to be proficient in the operation of the process control instruments, including how to calibrate them, how to interpret their readings, and how to diagnose and rectify faults.
Conclusion
Mastering process control instrumentation in cement plants is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. It requires a comprehensive understanding of the process, the control principles, and the operation of the process control instruments. However, with the right knowledge and skills, it can lead to significant improvements in the quality of the cement, the efficiency of the production process, and the overall profitability of the cement plant.
This guide provides a thorough overview of the importance of process control instrumentation in cement plants, the role of the monitoring control systems, the types of instrumentation used, and how to implement a control and instrumentation system. It is hoped that it will serve as a valuable resource for anyone involved in the cement industry, whether they are process engineers, control engineers, plant operators, or plant managers.




