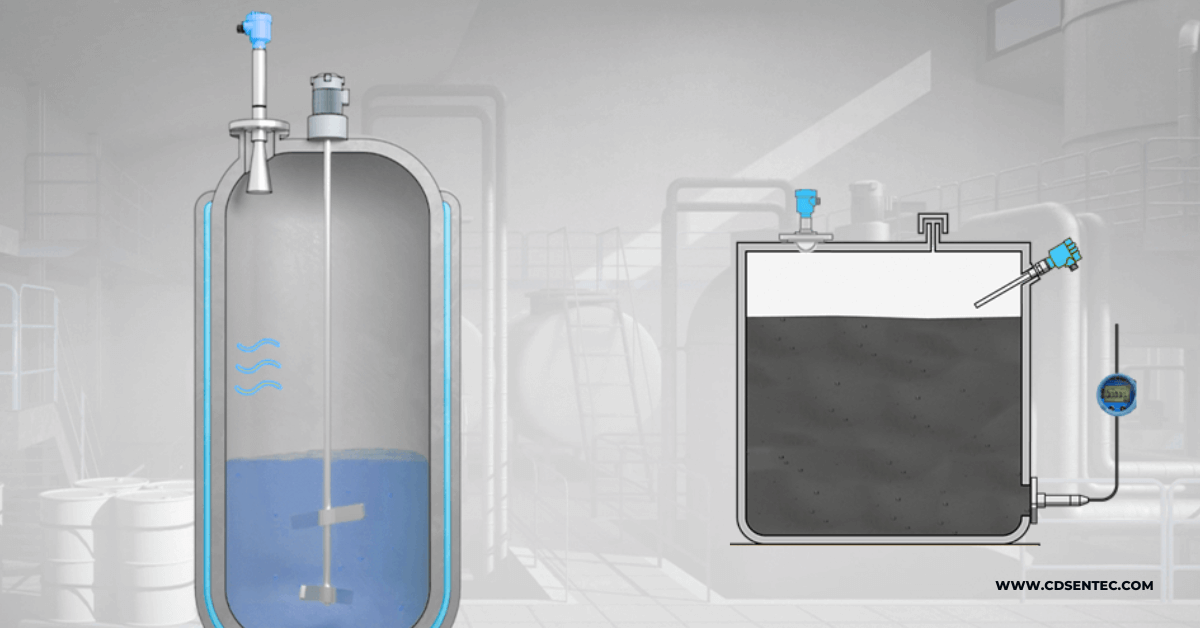
Pressure gauges are essential tools used in various industries to measure and monitor the pressure of liquids and gases. Accurate pressure measurements are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of different systems, such as pipelines, tanks, and industrial machinery. However, incorrect installation of pressure gauges can lead to inaccurate readings and potential safety hazards. In this article, we will demystify the process of pressure gauge installation and provide expert tips to ensure error-free measurements.
How are pressure gauges installed?
Proper installation of pressure gauges begins with selecting the appropriate location. The gauge should be installed at a point where it can accurately measure the pressure of the system. It is important to consider factors such as vibration, temperature, and accessibility when choosing the installation site.
Once the location is determined, the next step is to mount the pressure gauge. This typically involves attaching the gauge to a pipe or instrument panel using suitable mounting hardware. It is essential to ensure a secure and stable mounting to prevent any movement or vibrations that can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
After mounting the gauge, the next step is to connect it to the system being measured. This is done by attaching the pressure gauge to the system through a suitable connection, such as a threaded or flanged connection. It is important to use the correct type and size of connection to ensure a proper seal and prevent any leaks.
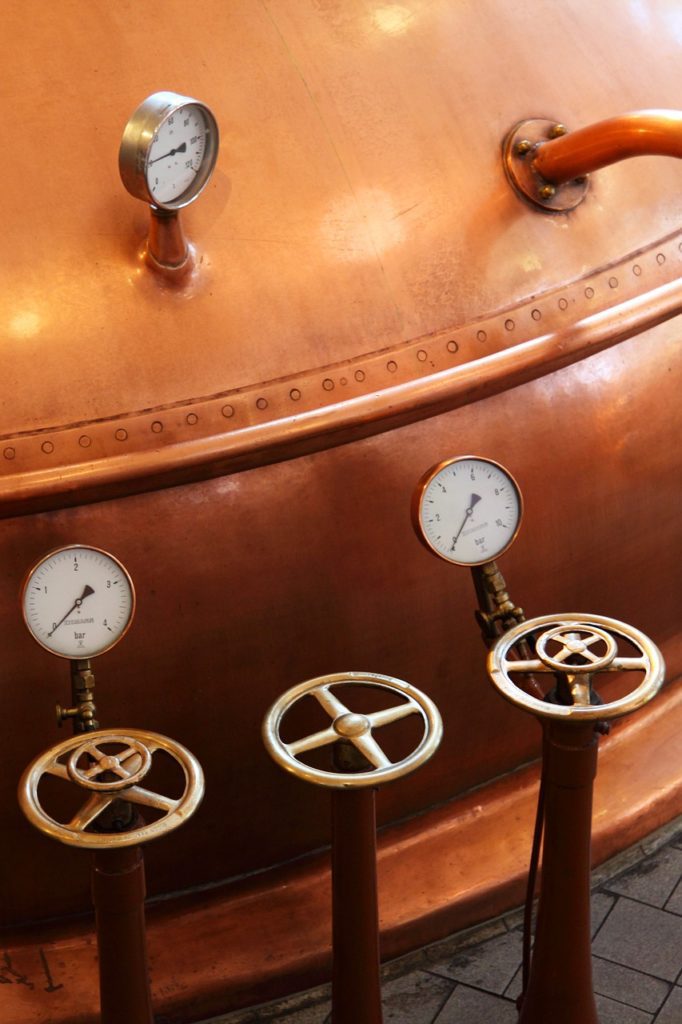

What is the installation height of a pressure gauge?
The installation height of a pressure gauge refers to the vertical distance between the gauge and the point where the pressure is being measured. This height is crucial for accurate pressure readings, as the pressure can vary with height due to gravitational forces.
In general, it is recommended to install the pressure gauge at the same height as the point of measurement. This ensures that the gauge is subjected to the same pressure as the system being measured, resulting in accurate readings. However, if it is not possible to install the gauge at the same height, corrections may need to be applied to account for the difference in height.
It is important to note that the installation height should be measured from the centerline of the gauge to the centerline of the point of measurement. This ensures consistency and accuracy in the pressure readings.
Do pressure gauges need to be mounted vertically?
While it is not mandatory to mount pressure gauges vertically, it is generally recommended for optimal performance. Mounting the gauge vertically helps minimize the effect of gravitational forces on the pressure measurement.
When pressure gauges are mounted horizontally or at an angle, the weight of the gauge and the fluid inside can affect the accuracy of the readings. This is particularly important in applications where precise pressure measurements are critical.
However, there are instances where mounting the gauge vertically may not be feasible due to space constraints or other practical considerations. In such cases, it is important to ensure that the gauge is properly calibrated and any necessary corrections are applied to account for the installation angle.
Common mistakes to avoid during pressure gauge installation
Improper installation of pressure gauges can lead to inaccurate measurements and potential safety hazards. To ensure error-free measurements, it is important to avoid the following common mistakes:
- Over-tightening: Applying excessive force while tightening the gauge connection can damage the gauge or cause leaks. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications to ensure proper tightening without causing any damage.
- Using incorrect sealant: Choosing the wrong type of pipe sealant or using too much sealant can result in leaks and compromise the accuracy of the measurements. It is crucial to select the appropriate sealant recommended by the manufacturer and apply it in the correct amount.
- Neglecting calibration: Pressure gauges should be regularly calibrated to maintain their accuracy. Neglecting calibration can lead to inaccurate measurements over time. It is important to establish a calibration schedule and follow it diligently to ensure reliable and precise readings.
3 precautions for pressure gauge installation
1.The selection of the pressure measuring point should reflect the true size of the measured pressure
①. It should be selected in the pipe section where the measured medium flows in a straight line, and should not be selected in the pipeline bends, bifurcations, dead ends or other places where vortices are easily formed.
②. When measuring the pressure of the flowing medium, the pressure point should be perpendicular to the flow direction, and the inner wall of the connection between the inner end face of the pressure pipe and the production equipment should be kept flush, and there should be no protrusions or burrs.
③. When measuring the pressure of liquid (gas), the pressure point should be at the lower (upper) part of the pipeline, so that no gas (liquid) is accumulated in the pressure guiding pipe.
2. Laying of pressure guiding pipes
①. The thickness of the pressure guiding tube should be appropriate, generally the inner diameter is 6-10mm, the length should be as short as possible, and the longest should not exceed 50m to reduce the delay of pressure indication. If it exceeds 50m, a pressure gauge that can be transmitted over a long distance should be selected.
②. The pressure guiding pipe should have an inclination of 1:10~1:20 when it is installed horizontally, so as to facilitate the discharge of the liquid (or gas) accumulated in it.
③. When the measured medium is easy to condense or freeze, it is necessary to add thermal insulation and heat tracing pipeline.
④. A shut-off valve should be installed between the pressure taking port and the pressure gauge, for the purpose of overhauling the pressure gauge. The shut-off valve should be installed close to the pressure taking port.
3. Installation of pressure gauge
①The pressure gauge should be installed in a place where it is easy to observe and repair.
②The installation site should try to avoid the influence of vibration and high temperature.
③ When measuring the steam pressure, a condensate pipe should be installed to prevent the high-temperature steam from directly contacting the pressure measuring element; for the pressure measurement of corrosive media, an isolation tank with a neutral medium should be added.
④ For the connection of the pressure gauge, an appropriate material should be selected according to the level of the measured pressure and the properties of the medium as a sealing gasket to prevent leakage.
⑤ When the measured pressure is small, and the pressure gauge and the pressure taking port are not at the same height, the measurement error caused by this height should be corrected according to Δp=±Hρg. where H is the height difference, ρ is the density of the medium in the pressure guiding tube, and g is the acceleration of gravity.
⑥For the sake of safety, in addition to selecting a pressure gauge for measuring high pressure with a vent hole, the case should be installed towards the wall or where no one passes to prevent accidents.
Troubleshooting common issues with pressure gauge installation
Even with proper installation and calibration, pressure gauge issues may still arise. Understanding and troubleshooting these common issues can help ensure accurate measurements. Here are some common issues and their possible solutions:
- Gauge reading fluctuations: Fluctuations in gauge readings can be caused by factors such as pulsations, vibrations, or clogged pressure connections. To address this issue, consider installing a pressure snubber or pulsation dampener to minimize the impact of pulsations. Ensure that pressure connections are clean and free from any debris or blockages.
- Gauge zero offset: A zero offset occurs when the gauge does not read zero at atmospheric pressure. This can be caused by misalignment, over-tightening, or internal damage. To correct the zero offset, check for proper alignment and ensure that the gauge connections are not over-tightened. If the issue persists, the gauge may need to be replaced or repaired.
- Gauge accuracy drift: Over time, pressure gauges may experience accuracy drift due to wear and tear or changes in the internal components. To address accuracy drift, regular calibration is essential to identify and correct any deviations. If the drift is significant and cannot be corrected through calibration, consider replacing the gauge.
Expert tips for error-free pressure measurements
To ensure error-free pressure measurements, consider the following expert tips:
- Select the right gauge: Choosing the right pressure gauge for the application is crucial. Consider factors such as the pressure range, media compatibility, accuracy requirements, and environmental conditions. Consult with experts or refer to industry standards to determine the most suitable gauge for specific applications.
- Follow manufacturer’s guidelines: Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for proper installation, calibration, and maintenance. Following these guidelines ensures that the gauge performs optimally and provides accurate measurements.
- Regular maintenance and inspection: Regularly inspect the pressure gauge for any signs of damage or wear. Clean the gauge and pressure connections to ensure proper functionality. Additionally, establish a maintenance schedule to address any potential issues and ensure the long-term reliability of the gauge.
Conclusion and final thoughts on pressure gauge installation best practices
Proper installation of pressure gauges is essential for accurate and reliable measurements. By following expert tips and best practices, such as selecting the right gauge, ensuring proper calibration, and troubleshooting common issues, errors can be minimized, and accurate measurements can be achieved. Remember to consult with manufacturers, industry experts, or calibration professionals for specific guidance and recommendations. By demystifying pressure gauge installation, this article aims to empower professionals to achieve error-free pressure measurements and enhance safety and efficiency in their respective industries.
If you need assistance with pressure gauge installation or have any questions, feel free to reach out to our team of experts. We are here to help you achieve accurate and reliable pressure measurements in your applications.