In this comprehensive guide, you will gain a deep understanding of guided wave radar technology and its various applications, advantages, troubleshooting issues, maintenance and calibration practices, industry-specific use cases, and best installation practices. By the end of this guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge to choose the right guided wave radar level gauge for their specific application and understand the future trends in this technology.
Understanding Guided Wave Radar Technology
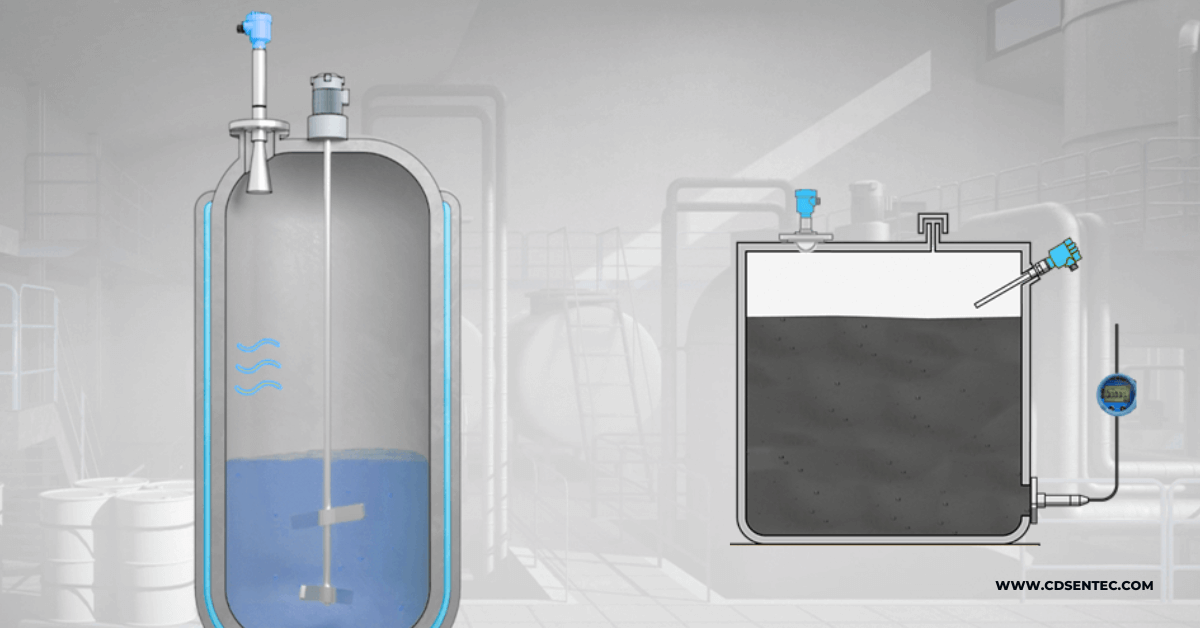
Guided wave radar technology is a cutting-edge method used for level measurement in various industrial applications. Unlike traditional level measurement techniques, guided wave radar level gauges utilize guided electromagnetic waves to accurately measure the level of liquids, solids, and interface levels. The basic principle behind guided wave radar technology involves the transmission of low-energy, high-frequency electromagnetic pulses along a probe or waveguide. These pulses travel down the probe, come into contact with the product being measured, and are reflected back to the instrument. By measuring the time-of-flight of these pulses, the level of the product can be precisely determined.
One of the key advantages of guided wave radar technology is its ability to provide accurate and reliable level measurements even in challenging process conditions. It can effectively measure levels in high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive environments, making it suitable for a wide range of industries such as oil and gas, chemical, power generation, and water treatment.
Applications of Guided Wave Radar Level Gauges
Guided wave radar level gauges find extensive application in various industrial processes where accurate level measurement is critical for operational efficiency and safety. These applications include but are not limited to, inventory management in storage tanks, monitoring of process vessels, and controlling the level of liquids and solids in silos and hoppers. In the oil and gas industry, guided wave radar level gauges are used for measuring the level of crude oil, condensate, and other hydrocarbons in storage tanks and separators.
The versatility of guided wave radar technology allows it to be used in a wide range of products, from aggressive chemicals and liquid hydrocarbons to powders and bulk solids. Its ability to handle varying dielectric constants and foam makes it an ideal choice for applications where other level measurement technologies may fall short. Additionally, the non-contact measurement principle of guided wave radar level gauges eliminates the need for direct contact with the measured product, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring reliable and accurate measurements.
Advantages of Guided Wave Radar Level Transmitters
Guided wave radar level transmitters offer several advantages over traditional level measurement technologies, making them a preferred choice for many industrial applications. One of the primary advantages is their ability to provide accurate and reliable measurements in challenging process conditions. Unlike ultrasonic or capacitance level transmitters, guided wave radar instruments are unaffected by factors such as temperature variations, pressure changes, and vapor spaces, ensuring consistent performance in diverse environments.

Another key advantage of guided wave radar level transmitters is their versatility in measuring different types of materials, including liquids, solids, and interface levels. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of industries and applications, eliminating the need for multiple level measurement devices. Additionally, guided wave radar technology offers precise and continuous level measurements, enabling real-time monitoring and control of processes, which is essential for optimizing production efficiency and ensuring safety.
Features of Rod Type Guided Wave Radar Level Gauge
The guided wave radar level gauge is divided into rod type and cable type. So what are the characteristics of the rod radar level gauge?
1. Low energy consumption. The waveguide of the liquid level gauge provides a fast and efficient channel for the round-trip transmission of the signal to the liquid level, and the attenuation of the signal is kept to a small degree, so it can be used to measure the medium liquid level with a particularly low dielectric constant. In addition, due to the low energy consumption of the guided wave radar, a loop power supply is used instead of a separate AC power supply, so a lot of installation costs are greatly saved.
2. Since the transmission of the signal in the waveguide will not be affected by the fluctuation of the liquid level and the obstacles in the storage tank, the return signal energy received by the liquid level gauge is relatively strong, and there are interfering stray signals in the return signal. It is very small and basically has no effect on the measurement signal.
3. The change of the dielectric constant of the medium has no obvious influence on the measurement performance of the liquid level gauge. Rod-type guided wave radar, like conventional radar, uses transit time to measure medium level, the only difference is the difference in signal amplitude (strength). Ordinary radar needs to consider the influence of the medium, it is difficult to identify the various signals returned, and it is impossible to distinguish the real liquid level signal from the stray signal, while the rod-type guided wave radar only needs to measure the transmission time of the electromagnetic wave, and does not need to be processed. and discriminating signals.
4. The change of medium density has no effect on the measurement of the liquid level gauge. The change of medium density affects the buoyancy of objects submerged in the medium, but does not affect the transmission of electromagnetic waves in the waveguide.
5. Mist and foam have no effect on the measurement of the level gauge. Since electromagnetic waves do not travel through space, fog does not affect signal attenuation, and foam does not scatter the signal and lose energy.
6. The deposition and contamination of the medium on the waveguide have very little influence on the liquid level measurement.
7. The maximum range of the rod type radar level gauge can reach 6 meters.
Reasons for fluctuation of guided wave radar level gauge measurement
1. The fluctuation of the medium will cause the reading of the guided wave radar level gauge to fluctuate. This phenomenon is caused by process variation and is therefore not an instrument failure. Generally, after the medium fluctuation stops, the reading of the guided wave radar level gauge will return to normal.
2. The guided wave strength of the guided wave radar level gauge is too strong or too weak, resulting in large fluctuations in the reading.
3. The steel cable of the guided wave radar level gauge is loosely installed or has no counterweight, which is easy for the steel cable to swing and collide with the inner wall of the equipment, resulting in large fluctuations in the indication of the level gauge.
4. The installation position of the steel cable of the guided wave radar level gauge is too close to the inner wall of the equipment, and it is easy for the steel cable to swing and collide with the inner wall of the equipment.
5. The blind area of the guided wave radar level gauge is too small.
6. The installation position of the guided wave radar level gauge is close to the feed inlet, and the feed scours the steel cable, causing the indication of the guided wave radar level gauge to fluctuate.
Troubleshooting of Fluctuations of Guided Wave Radar Liquid Level Gauge
1. The blind zone setting of the guided wave radar level gauge should be adjusted according to the site requirements.
2. Adjust the guided wave strength of the guided wave radar level gauge according to the site requirements.
3. When installing the steel cable of the guided wave radar level gauge, it should be tightened and fixed, or reconfigured.
4. Add a counterweight (such as a heavy hammer) to the bottom of the steel cable of the guided wave radar level gauge, so that the steel cable will not shake during the measurement process.
5. The installation position of the guided wave radar level gauge needs to avoid the feed inlet and maintain a proper distance from the tank wall.
Maintenance and Calibration of Guided Wave Radar Instruments
Proper maintenance and calibration are essential to ensure the continued accuracy and reliability of guided wave radar instruments. Regular inspection of the probe or waveguide for any buildup or damage is crucial to prevent signal interference and ensure accurate level measurements. Additionally, calibration of the instrument to account for variations in dielectric constants of different materials is necessary to maintain measurement accuracy.
During maintenance and calibration procedures, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations to ensure the proper functioning of the guided wave radar instrument. This may include performing zero and span checks, verifying the integrity of the signal processing unit, and calibrating the instrument to the specific process conditions and materials being measured. By adhering to a comprehensive maintenance and calibration schedule, users can maximize the lifespan of their guided wave radar instruments and minimize the risk of measurement errors.
Choosing the Right Guided Wave Radar Level Gauge for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate guided wave radar level gauge for a specific application is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable level measurements. Factors such as the type of measured product, process conditions, required measurement range, and installation constraints must be carefully considered when choosing a guided wave radar instrument. It is essential to assess the dielectric constant and conductivity of the measured material, as well as the operating temperature and pressure, to select a suitable guided wave radar level gauge that can effectively handle these parameters.
Additionally, understanding the installation requirements and environmental conditions of the application site is essential for choosing the right guided wave radar instrument. Factors such as vessel size, mounting options, and potential obstructions must be taken into account to ensure proper installation and optimal performance of the level gauge. Consulting with experienced application engineers and level measurement experts can provide valuable insights into selecting the most suitable guided wave radar instrument for specific industrial applications, ensuring accurate and reliable level measurements.
Conclusion and Future Trends in Guided Wave Radar Technology
In conclusion, guided wave radar technology offers a powerful and reliable solution for level measurement in a wide range of industrial applications. Its ability to provide accurate and continuous level measurements in challenging process conditions, along with its versatility and minimal maintenance requirements, makes it a preferred choice for many industries. As technology continues to advance, future trends in guided wave radar technology are expected to focus on enhanced signal processing algorithms, improved materials for waveguides and probes, and integration with digital communication protocols for seamless connectivity with control and monitoring systems.
As industries strive for greater efficiency, safety, and sustainability, guided wave radar technology is poised to play a pivotal role in meeting these demands by providing precise and reliable level measurements for critical processes. By staying abreast of the latest developments and innovations in guided wave radar technology, industrial users can leverage this advanced level measurement technology to optimize their operations and achieve higher levels of productivity and safety.
CTA: For more information on guided wave radar level gauges and expert guidance in selecting the right solution for your application, contact SenTec today.