In the world of industrial processes, accurate measurement and control of flow are crucial for ensuring optimal efficiency and productivity. One key tool that plays a vital role in this regard is the thermal mass flow meter. This innovative device is designed to measure the flow rate of various fluids, including liquids, gases, and steam, by utilizing the principle of thermal dispersion. By understanding how thermal mass flow meters work and their various applications, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right one for your industrial needs.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Working Principle
Thermal mass flow meters operate on the principle of thermal dispersion, which utilizes the difference in heat transfer rates between a heated sensor and the fluid flowing over it. The meter consists of two temperature sensors: one is heated, and the other is temperature-compensated. As the fluid flows over the heated sensor, it absorbs heat, causing a temperature difference between the two sensors. By measuring the temperature difference, the thermal mass flow meter can accurately calculate the mass flow rate of the fluid.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Calculation
To calculate the mass flow rate using a thermal mass flow meter, several factors need to be taken into consideration. These factors include the temperature difference between the two sensors, the density of the fluid, and the specific heat capacity of the fluid. By using these parameters and applying the appropriate formulas, the thermal mass flow meter can provide accurate measurements of the mass flow rate in real-time. This data is invaluable for industries that require precise control over their fluid flow processes.
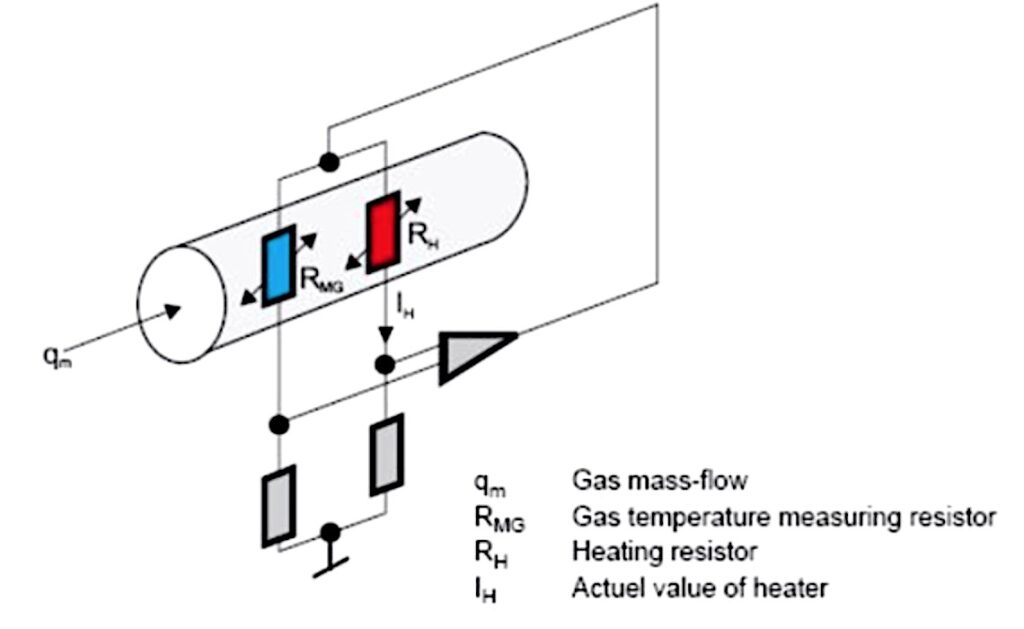
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Diagram
A thermal mass flow meter consists of several key components that work together to measure the flow rate of fluids. The diagram below illustrates the basic structure of a thermal mass flow meter:

- Flow Body: This is the main housing of the flow meter that directs the fluid flow through the meter.
- Temperature Sensors: The flow meter contains two temperature sensors – one heated and one temperature-compensated – that measure the temperature difference caused by the flowing fluid.
- Electronics: The electronics module processes the signals from the temperature sensors and calculates the mass flow rate.
- Display: The display unit provides real-time readings of the mass flow rate and other relevant data.
Understanding the different components of a thermal mass flow meter is essential for selecting the right one for your specific industrial needs.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Correction Factor
It is important to note that the accuracy of a thermal mass flow meter can be affected by various factors, such as changes in fluid composition, flow conditions, and temperature. To compensate for these influences, a correction factor is often applied to the meter’s measurements. The correction factor is determined through calibration and ensures that the meter provides accurate readings under different operating conditions. When choosing a thermal mass flow meter, it is crucial to consider the correction factor and its impact on the overall accuracy of the device.
Coriolis vs Thermal Dispersion Mass Flow Meter
When it comes to flow measurement, two commonly used technologies are Coriolis and thermal dispersion mass flow meters. While both methods have their merits, there are distinct differences between the two.
Coriolis flow meters operate based on the principle of fluid mass-induced tube vibration. As the fluid flows through the vibrating tubes, the Coriolis force causes a phase shift in the tubes, which is directly proportional to the mass flow rate. Coriolis flow meters are known for their high accuracy and ability to measure a wide range of fluids. However, they can be costly and may require additional maintenance.
On the other hand, thermal dispersion mass flow meters, as discussed earlier, rely on the principle of heat transfer. They are generally more cost-effective, easier to install, and require minimal maintenance. However, thermal mass flow meters may have limitations in measuring certain types of fluids and may not provide the same level of accuracy as Coriolis flow meters. When choosing between the two, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of your industrial application and weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each technology.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Advantages and Disadvantages
Like any other technology, thermal mass flow meters have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision when selecting the right flow meter for your industrial needs.
Advantages of Thermal Mass Flow Meters:
- Wide Range of Applications: Thermal mass flow meters can be used in a variety of industries, including oil and gas, chemical, pharmaceutical, and food processing. They are suitable for measuring the flow rates of liquids, gases, and steam.
- Cost-Effective: Thermal mass flow meters are generally more affordable compared to other flow measurement technologies, making them a cost-effective choice for many industries.
- Easy Installation: These flow meters are relatively easy to install, requiring minimal piping modifications or additional equipment.
- Low Maintenance: Thermal mass flow meters do not have moving parts, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Disadvantages of Thermal Mass Flow Meters:
- Fluid Limitations: Thermal mass flow meters may not be suitable for measuring certain types of fluids, such as highly corrosive substances or fluids with low thermal conductivity.
- Accuracy Limitations: While thermal mass flow meters provide accurate measurements in many applications, they may not offer the same level of precision as some other flow measurement technologies.
- Calibration Requirements: To ensure accurate readings, thermal mass flow meters may require periodic calibration, which can add to the overall maintenance costs.
When considering the advantages and disadvantages of thermal mass flow meters, it is crucial to evaluate your specific industrial requirements and determine whether these flow meters align with your needs.
Inline Thermal Mass Flow Meter vs Insertion Thermal Mass Flow Meter
When choosing a thermal mass flow meter, you will come across two primary types: inline and insertion flow meters. Each type has its own set of advantages and considerations, depending on your industrial application.
Inline Thermal Mass Flow Meter:
Inline thermal mass flow meters are designed to be installed directly in the pipeline, allowing for continuous measurement of the fluid flow. These meters provide real-time readings and are suitable for applications that require instantaneous flow rate monitoring. Inline flow meters are compact, require minimal space, and are relatively easy to install. However, they may be more expensive compared to insertion flow meters.
Insertion Thermal Mass Flow Meter:
Insertion thermal mass flow meters, as the name suggests, are inserted into the pipeline through a hole or a tapping point. These meters are ideal for applications where continuous measurements are not necessary and where cost is a significant consideration. Insertion flow meters can be installed and removed without interrupting the flow process, making them a flexible choice for temporary or periodic flow rate measurements. However, they may require more installation time and effort compared to inline flow meters.
When deciding between an inline and an insertion thermal mass flow meter, consider factors such as cost, installation requirements, and the need for continuous or periodic flow rate measurement.
Different Types of Thermal Mass Flow Meters
Thermal mass flow meters come in various configurations to suit different industrial applications. Some of the commonly used types include:
Thermal Mass Flow Meter for Air
Air flow measurement is crucial in various applications, including HVAC systems, cleanrooms, and industrial ventilation. Thermal mass flow meters offer a reliable and accurate solution for measuring the flow rates of air. These flow meters can be used to monitor air flow in ducts, stacks, or open spaces. The ability to measure both high and low flow rates makes thermal mass flow meters suitable for a wide range of air flow applications.
When selecting a thermal mass flow meter for air, consider factors such as the required flow range, accuracy, and environmental conditions. Additionally, ensure that the flow meter is specifically designed and calibrated for air flow measurements.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter for Liquids
In addition to gas flow measurement, thermal mass flow meters can also be used to measure the flow rates of liquids. These flow meters are particularly useful in applications where the flow rates of viscous or non-conductive liquids need to be monitored. Thermal mass flow meters for liquids typically have specialized sensor designs and materials to ensure accurate measurements.
When selecting a thermal mass flow meter for liquids, consider the specific characteristics of the liquid, such as viscosity and conductivity, as well as the required flow range and accuracy. Ensure that the flow meter is designed and calibrated for liquid flow measurement.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter for Natural Gas
Natural gas is a widely used fuel source in various industries, including power generation, heating, and manufacturing. Accurate measurement of natural gas flow rates is crucial for billing, process control, and environmental compliance. Thermal mass flow meters offer a reliable and cost-effective solution for measuring natural gas flow rates.
When selecting a thermal mass flow meter for natural gas, consider factors such as the required flow range, pressure, and temperature conditions. Additionally, ensure that the flow meter is specifically designed and calibrated for natural gas flow measurement.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter for Steam
Steam is a common medium used for heating, power generation, and industrial processes. Measuring the flow rate of steam accurately is essential for ensuring efficient operation and energy management. Thermal mass flow meters provide a reliable solution for measuring steam flow rates.
When selecting a thermal mass flow meter for steam, consider factors such as the required flow range, pressure, and temperature conditions. Additionally, ensure that the flow meter is specifically designed and calibrated for steam flow measurement.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Applications
Thermal mass flow meters find extensive applications in various industries due to their versatility and ability to measure different types of fluids. Some of the common applications include:
- Oil and Gas Industry: Thermal mass flow meters are used for measuring the flow rates of natural gas, crude oil, and other hydrocarbon fluids in pipelines and refineries.
- Chemical Industry: These flow meters are employed to measure the flow rates of various chemicals, including corrosive and hazardous substances.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Thermal mass flow meters are utilized in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes to measure and control the flow rates of liquids and gases.
- Food Processing Industry: These flow meters play a crucial role in measuring the flow rates of food and beverage products, ensuring accurate dosing and mixing.
- Environmental Monitoring: Thermal mass flow meters are used in environmental monitoring systems to measure and control the flow rates of gases, such as air quality monitoring or gas emissions.
These are just a few examples of the wide-ranging applications of thermal mass flow meters. When selecting a flow meter for your industrial needs, consider the specific requirements and conditions of your application to ensure the optimal performance of the meter.
Thermal Mass Flow Meter Installation Guidelines
Proper installation of a thermal mass flow meter is crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable measurements. Here are some general guidelines to follow when installing a thermal mass flow meter:
- Position: Install the flow meter in a location where the fluid flow is fully developed and free from disturbances, such as bends or obstructions.
- Orientation: Ensure that the flow meter is installed in the correct orientation, as specified by the manufacturer. Incorrect orientation can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
- Piping Considerations: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for piping requirements, such as upstream and downstream straight pipe lengths, to ensure proper flow conditions.
- Electrical Connections: Ensure that the electrical connections are secure and properly grounded to minimize the risk of electrical interference.
- Calibration: Calibrate the flow meter according to the manufacturer’s guidelines to ensure accurate measurements. Periodic calibration may be required to maintain the accuracy of the flow meter.
Following these installation guidelines will help optimize the performance of the thermal mass flow meter and ensure accurate flow rate measurements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Thermal Mass Flow Meter
When selecting a thermal mass flow meter for your industrial needs, several factors need to be considered to ensure the optimal performance of the device. Here are some key factors to keep in mind:
- Fluid Properties: Consider the specific properties of the fluid, such as composition, viscosity, and thermal conductivity. Ensure that the flow meter is suitable for measuring the flow rate of the fluid.
- Flow Range: Determine the expected flow range of the fluid and select a flow meter that can accurately measure within that range.
- Accuracy Requirements: Evaluate the required level of accuracy for your application. Different flow meters offer varying degrees of accuracy, so choose one that meets your specific requirements.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider the temperature, pressure, and humidity conditions in which the flow meter will operate. Ensure that the flow meter is designed to withstand these conditions.
- Installation and Maintenance: Evaluate the installation and maintenance requirements of the flow meter. Consider factors such as ease of installation, access for maintenance, and calibration requirements.
- Budget Considerations: Determine your budget for the flow meter and select a device that provides the required performance within your budget constraints.
By considering these factors, you can choose a thermal mass flow meter that is best suited for your industrial needs and ensures accurate flow rate measurements.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Thermal Mass Flow Meter for Your Industrial Needs
Selecting the right thermal mass flow meter for your industrial needs is crucial for accurate and efficient flow measurement. By understanding how thermal mass flow meters work and considering factors such as installation guidelines, application requirements, and manufacturer reliability, you can make an informed decision. Remember to consult with experts and take advantage of the vast range of thermal mass flow meter options available in the market. With the right thermal mass flow meter, you can optimize your industrial processes and achieve accurate flow measurement.
CTA: If you need assistance in choosing the right thermal mass flow meter for your industrial needs, contact us today for expert guidance and support.




