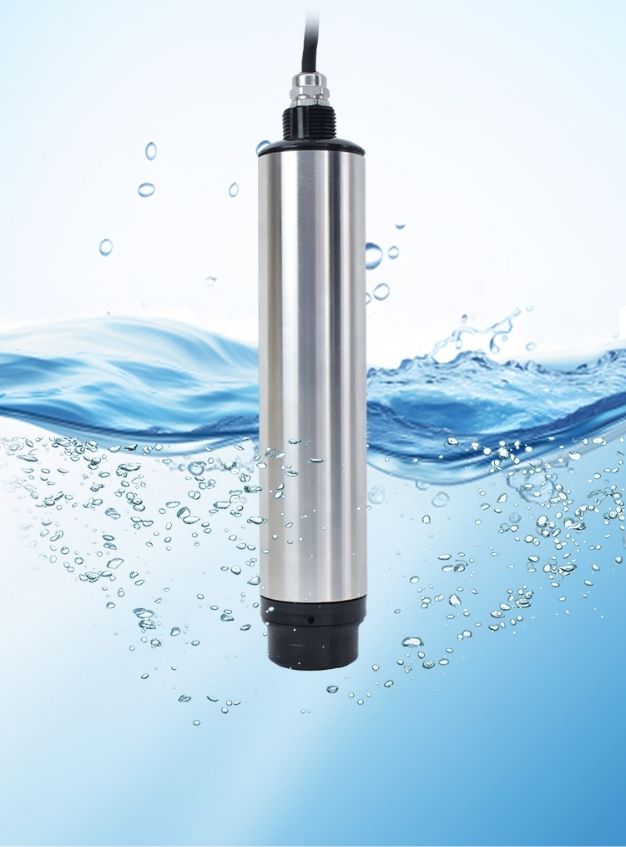
The thermal resistance is designed and manufactured by using the basic principle that the resistance value of platinum wire changes with the change of temperature. It is divided into 10 ohms (grading number Pt10) and 100 ohm (graduation number is Pt100), etc., the temperature measurement range is large, suitable for -200~850 ℃. The temperature sensing element of the 10 ohm platinum thermal resistance is made of thick platinum wire, and the temperature resistance is obvious. The platinum thermal resistance better than 100 ohm is mainly used in the temperature zone above 650 ℃: 100 ohm platinum thermal resistance is mainly used in the temperature zone below 650 ℃, although it can also be used in the temperature zone above 650 ℃, but in the temperature above 650 ℃ A-level errors are not allowed in the zone.
What is thermal resistance temperature sensor ?
The resistance varies according to the temperature. The platinum resistance is connected to the circuit, and the change of resistance can be known by observing the change of current. By recording the currents at different temperatures and drawing a temperature-resistance diagram, the value of the temperature can be inferred when the resistance is known.
What is Armored thermal resistance temperature sensor ?
Armored thermal resistance is a kind of temperature sensor, which uses the characteristics of the resistance of the material to change when the temperature changes to measure the temperature. When the resistance value changes, the working instrument will display the temperature value corresponding to the resistance value. It is smaller in diameter and easier to bend than the assembled platinum resistance, and is suitable for installation in special occasions such as narrow pipelines and fast response and miniaturization. It can automatically detect gases, liquid media and solid surfaces in the temperature range of -200~600 °C, and can be directly connected with copper wires and secondary instruments.
PLATINUM THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR MEASUREMENT PRINCIPLE
The thermal resistance temperature measurement is based on the characteristic that the resistance value of metal conductor increases with the increase of temperature. When the resistance value changes, the working instrument will display the temperature value corresponding to the thermal resistance.
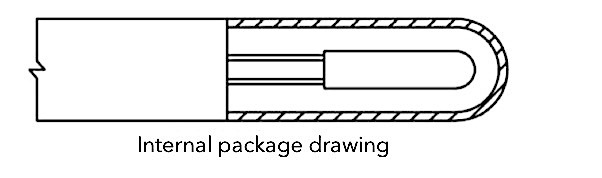
Thermal resistance thermometry is based on the characteristic that the resistance value of metal conductors increases with temperature. Thermal resistors are mostly made of pure metal materials, and platinum and copper are the most widely used. In addition, nickel, manganese and rhodium have been used to manufacture thermal resistors.
What are the advantages of armored thermal resistance?
Armored thermal resistance: its outer diameter is generally φ2~φ8mm, and the minimum can reach φmm. Compared with ordinary thermal resistance, it has the following advantages:
①Small volume, no air gap inside, and small measurement lag in terms of thermal inertia;
②Good mechanical properties, vibration resistance and impact resistance;
③Can be bent, easy to install
④Long service life.
What is the temperature graduation number?
The temperature graduation number is a standard sequence used to reflect the temperature change of the temperature sensor in the measurement temperature range corresponding to the change of the sensor voltage or resistance value, that is, the temperature value corresponding to the thermal resistance, thermocouple, resistance, and potential. The thermal resistance graduation numbers mainly include platinum resistances such as Pt100, Pt1000, Pt10, Pt800, and Pt500; copper resistances such as Cu50, Cu100, and Cu10; nickel resistances such as nickel NI120, NI500, and NI1000, as well as the very useful BA1, BA2, and G53.
Among them, the temperature measurement range of platinum resistance is -200~850℃, and the temperature measurement range of copper resistance is -50~150℃.
What is the working method of the RTD signal connection?
Thermal resistance is a primary element that converts temperature changes into resistance value changes, and usually needs to transmit resistance signals to computer control devices or other primary instruments through leads. The industrial thermal resistance is installed at the production site, and there is a certain distance between it and the control room, so the lead wire of the thermal resistance will have a greater impact on the measurement results.
There are three main ways to lead the thermal resistance
○1 Two-wire system: The method of connecting a wire at each end of the thermal resistance to draw out the resistance signal is called the two-wire system: this lead method is very simple, but because the connecting wire must have a lead resistance r, the size of r is related to the material and the wire. The length is related to the factor, so this lead method is only suitable for occasions with low measurement accuracy
○2 Three-wire system: The method of connecting a lead at one end of the root of the thermal resistance and connecting two leads at the other end is called a three-wire system. This method is usually used in conjunction with a bridge, which can better eliminate the influence of lead resistance. It is the most commonly used in industrial process control.
○3 Four-wire system: The method of connecting two wires at each end of the root of the thermal resistance is called a four-wire system, in which two leads provide a constant current I for the thermal resistance, convert R into a voltage signal U, and then pass the other two The root lead leads U to the secondary meter. It can be seen that this lead method can completely eliminate the influence of lead resistance, and is mainly used for high-precision temperature detection.
The thermal resistance adopts the three-wire connection method. The three-wire system is used to eliminate the measurement error caused by the resistance of the connecting wires. This is because the circuit for measuring the RTD is generally an unbalanced bridge. The thermal resistance is used as a bridge arm resistance of the bridge, and its connecting wire (from the thermal resistance to the central control room) also becomes a part of the bridge arm resistance. This part of the resistance is unknown and changes with the ambient temperature, resulting in measurement errors. Using a three-wire system, one wire is connected to the power end of the bridge, and the other two are connected to the bridge arm where the thermal resistance is located and the bridge arm adjacent to it, which eliminates the measurement error caused by the wire line resistance.
PLATINUM THERMISTOR TEMPERATURE SENSOR APPLICATION
1. Thermal resistance sensor application:
Temperature is a physical quantity that characterizes the degree of cold and heat of an object, and is a very important and common measurement parameter in the process of industrial and agricultural production. Temperature measurement and control play a very important role in ensuring product quality, improving production efficiency, saving energy, producing safety, and promoting the development of the national economy. Due to the ubiquity of temperature measurement, the number of temperature sensors ranks first among various sensors, accounting for about 50%.
A temperature sensor measures indirectly by an object changing a certain characteristic as the temperature changes. The characteristics of many materials and components change with temperature, so there are quite a few materials that can be used as temperature sensors. Temperature sensors cause physical parameters to change with temperature: expansion, resistance, capacitance, electromotive force, magnetic properties, frequency, optical properties, thermal noise, and so on.
Due to the extremely wide range of temperature measurement in industrial and agricultural production, from a few hundred degrees below zero to several thousand degrees above zero, temperature sensors made of various materials can only be used within a certain temperature range.
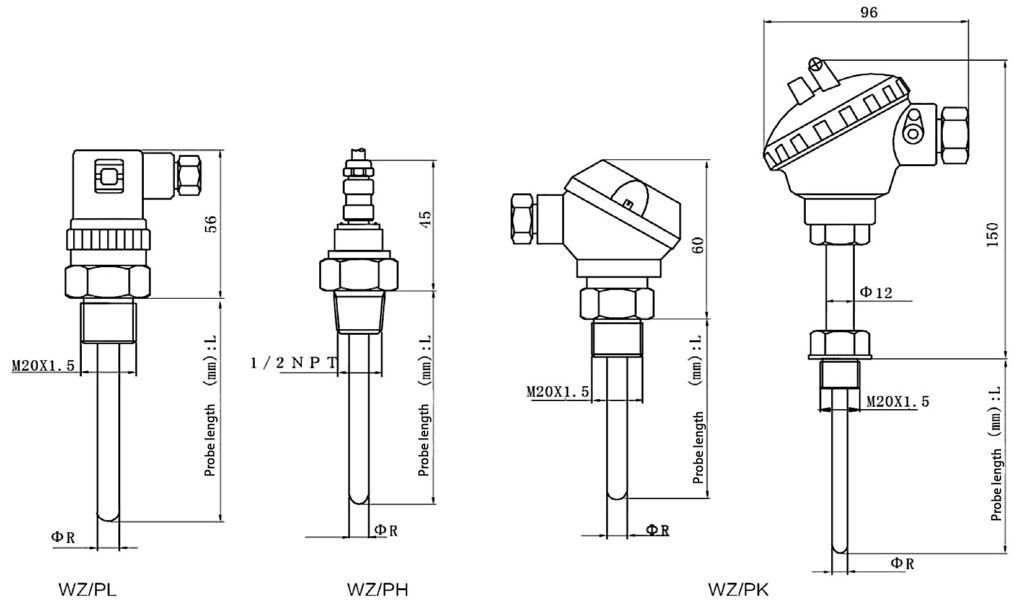
2. The main types of thermal resistance:
①Ordinary thermal resistance
From the temperature measurement principle of the thermal resistance, the change of the measured temperature is directly measured by the change of the resistance of the thermal resistance. Therefore, the change of the resistance of various wires such as the lead wire of the thermal resistance will affect the temperature measurement.
②End surface thermal resistance
The end-face thermal resistance temperature-sensing element is wound by a specially treated resistance wire, which is closely attached to the end face of the thermometer. Compared with general axial thermal resistance, it can reflect the actual temperature of the measured end surface more accurately and quickly. It is suitable for measuring the end surface temperature of bearing bushes and other mechanical parts.
③Armored thermal resistance
The armored thermal resistance is a solid body composed of temperature sensing elements (resistors), lead wires, insulating materials, and stainless steel sleeves. Its outer diameter is generally φ2–φ8mm, and the smallest can reach φmm.
④Explosion-proof thermal resistance
Explosion-proof thermal resistance through the junction box of special structure, the explosion of explosive mixed gas inside the shell due to the influence of sparks or arcs is confined in the junction box, and the production site will not cause excessive explosion. Explosion-proof thermal resistance can be used for temperature measurement in places with explosion hazard in Bla-B3c level zone.




